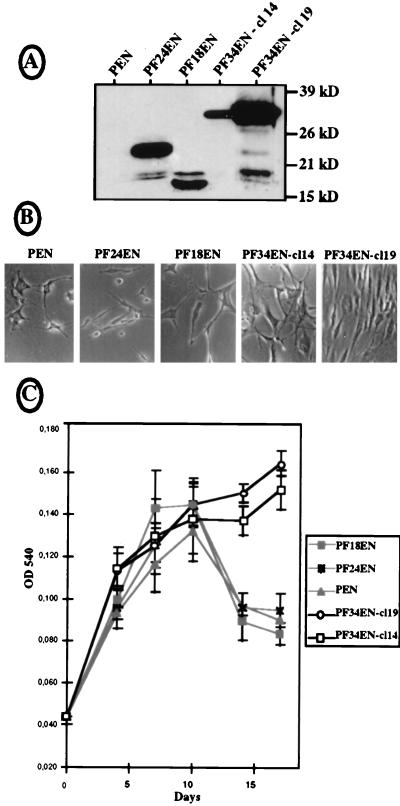
FIG. 8.
Expression of the different FGF-2 isoforms in permanently transfected NIH 3T3 cells. NIH 3T3 cells were transfected with bicistronic vectors expressing the 24-kDa (pF24EN), the 18-kDa (pF18EN), or the 34-kDa (pF34EN) FGF-2 or no protein (pEN) from their first cistrons and the neomycin resistance gene from their second cistrons; 10 to 12 G418-resistant clones were kept for each transfection, and analyses were performed with at least three clones of each origin. Two clones expressing two different levels of 34-kDa FGF-2 (cl14 and cl19), and one clone expressing a medium level of FGF-2, chosen for 24- and 18-kDa FGF-2 expression, are shown as representative clones. (A) Western immunoblotting was performed with cell extracts of the different clones, using anti-FGF-2 antibody as for Fig. 1. Positions of size standards are represented on the right. (B) Phase-contrast microscopy examination (magnification, ×100) of the different cell clones after 14 days of cultivation in six-well plates in 1% CS (see Materials and Methods). The panels correspond to representative parts of the culture dishes. (C) Proliferation curves obtained by the crystal violet method for cells seeded in 96-well plates and cultivated for 17 days (see Materials and Methods). In this procedure, cell growth is measured by determining the optical density at 540 nm (OD 540). Experiments were done in quadruplicate; they were also reproduced several times in triplicate with the classical cell counting procedure, which always gave similar results (not shown).