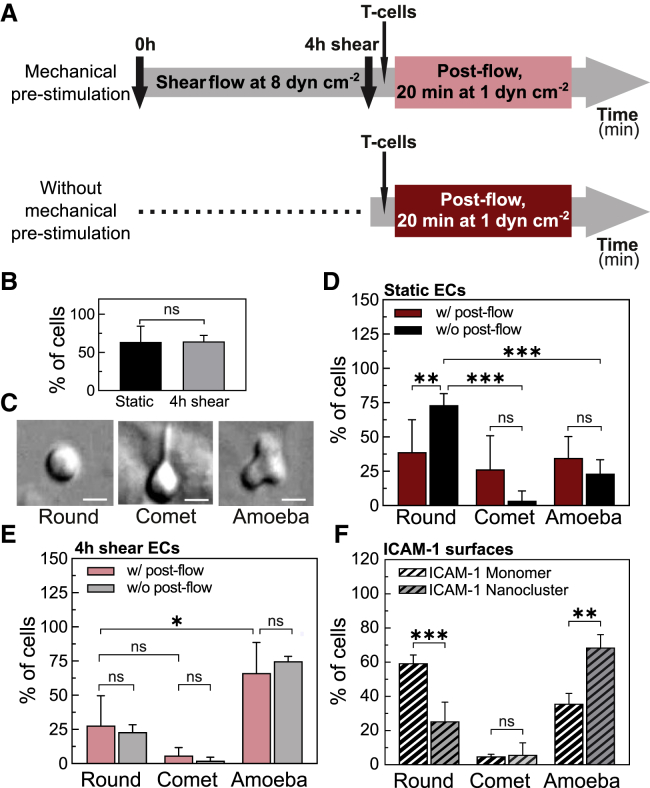
Figure 5.
Prolonged shear stimulation of ECs promotes a promigratory phenotype in T cells. (A) Scheme showing the characteristic timescales and course of the experiments with (top) and without shear-flow prestimulation of ECs (bottom). (B) Percentage of T cells that remained adhered to ECs after 20 min of postflow application. Results are mean ± SD on N = 13 and N = 5 independent experiments for static and 4 h sheared ECs, respectively (at least n = 10 cells (static) and n = 100 cells (4 h shear) per experiment. Significance has been calculated across N. (C) DIC images showing the three main cell morphologies observed: “round,” “comet-like,” and “amoeba-like.” Scale bars, 4 μm. (D) Percentage of T cells with indicated morphology adhered on static ECs (i.e., without mechanical prestimulation), with (w/, red) and without (w/o, black) postflow for 20 min. Results are mean ± SD on N = 6 and N = 4 independent experiments for w/ and w/o postflow, respectively (at least n = 10 T cells per experiment). Significance has been calculated across N. (E) Percentage of T cells with indicated morphology adhered to 4 h, shear-flow preconditioned ECs, with (w/, light red) and without (w/o, gray) postflow for 20 min. Results are mean ± SD on N = 5 and N = 4 independent experiments for w/ and w/o postflow, respectively (at least n = 10 T cells per experiment). Significance has been calculated across N. (F) Percentage of T cells with indicated morphology adhered to monomeric or nanoclustered ICAM-1-coated glass substrates. Results are mean ± SD on n = 60 cells (monomeric ICAM-1 substrates) and n = 57 cells (nanoclustered ICAM-1 substrates) for one representative experiment per condition. Significance has been calculated within the experiment shown. N = 3 independent experiments per condition ∗∗∗p < 0.001; ∗∗p = 0.01; ∗p = 0.1; ns, not significant. To see this figure in color, go online.