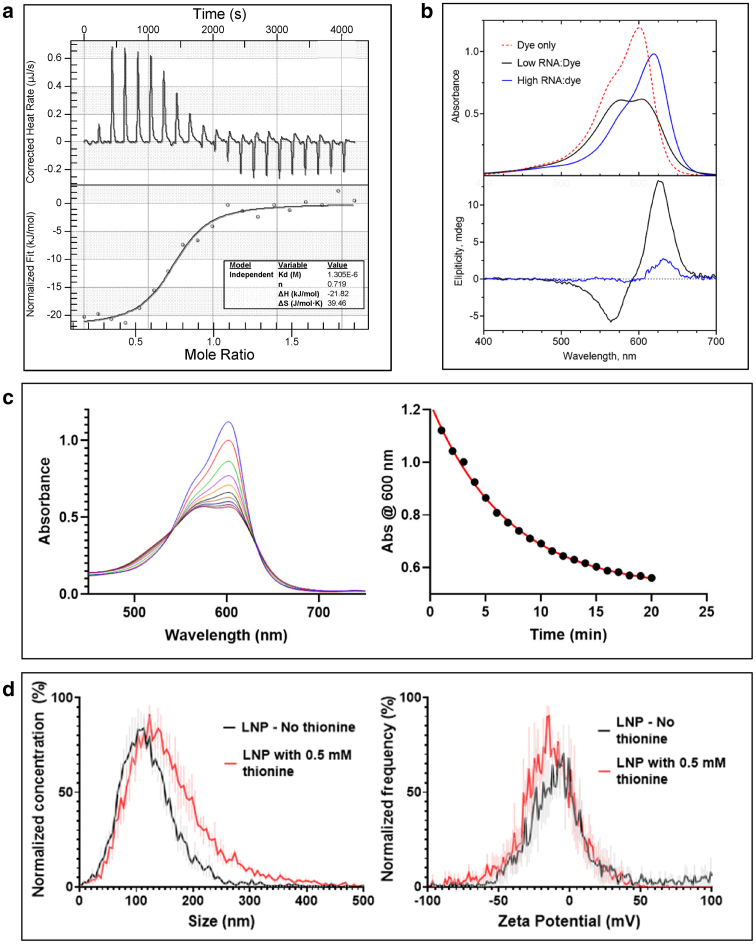
Figure 1.
Characterization of dye-binding and permeation. (a) Isothermal titration calorimetry of thionine titrated into mRNA. (Top) Raw data. (Bottom) Integrated heats of each injection versus molar ratio of thionine/nucleotide together with a fit using a one-site binding model. (b) Optical signatures of the thionine-mRNA binding interaction. Visible absorption spectra (top) of thionine at 0.0255 mM recorded in the absence of mRNA and in the presence of mRNA at low (4) and high (160) nucleotide/dye molar ratios (P/D). Corresponding circular dichroism (CD) spectra (bottom) show that at low P/D, the thionine absorption bands are resolved into negative and positive CD bands with extrema at 565 and 628 nm, respectively, whereas at high P/D, the induced CD is weak and characterized by a single positive band at 632 nm. (c) Dye permeation kinetics corresponding to mRNA-LNP added to a thionine solution. (Left) Scanning kinetics showing the spectral change as a function of time with scans taken at 2-min intervals. (Right) Kinetic time course of 600 nm absorbance together with a fit (red) to a first-order process with a rate constant of k = 0.143 min−1. (d) Nanoparticle tracking analysis of mRNA-LNP in the presence and absence of 0.5 mM thionine, showing small or insignificant effects of thionine on particle size and charge. Data represent the mean and error of 3 independent samples. (Left) Size distribution. (Right) ζ potential distribution.