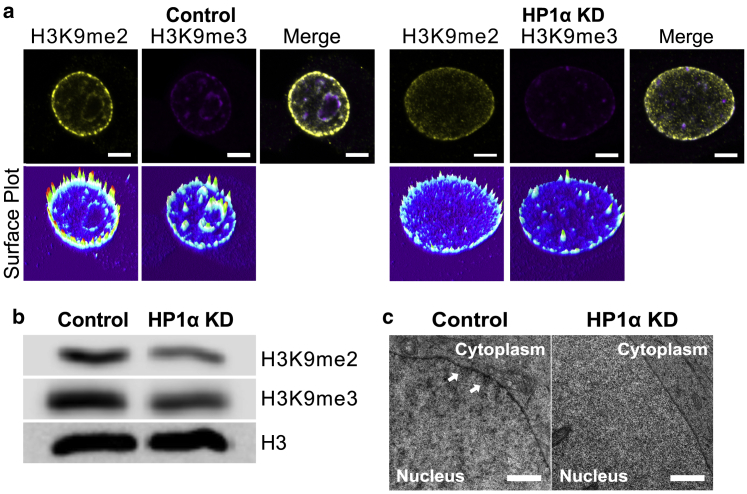
Figure 3.
Knockdown of HP1α disrupts heterochromatin organization in MCF7 cells. (a) Representative immunofluorescence confocal microscopy images of MCF7 control (left panel) and MCF7 HP1α KD cells (right panel) stained with antibodies against markers of heterochromatin, dimethylation of lysine 9 on histone H3 (H3K9me2) (yellow), and trimethylation of lysine 9 on histone H3 (H3K9me3) (magenta) are shown. Fluorescence surface plots of the medial slices through the nuclei (above) demonstrate the intensity of antibody staining. Scale bars, 5 μm. Additional images of cells are presented in Fig. S5. (b) Immunoblot analysis of extracted histones from MCF7 control and HP1α KD cells probed with antibodies against H3K9me2 and H3K9me3. An antibody against histone H3 is used as a loading control. (c) Representative electron micrographs showing regions of compact heterochromatin at the nuclear periphery in MCF7 control cells (white arrows), whereas the nuclei of MCF7 HP1αKD cells have a more diffuse chromatin patterning. Scale bars, 500 nm. To see this figure in color, go online.