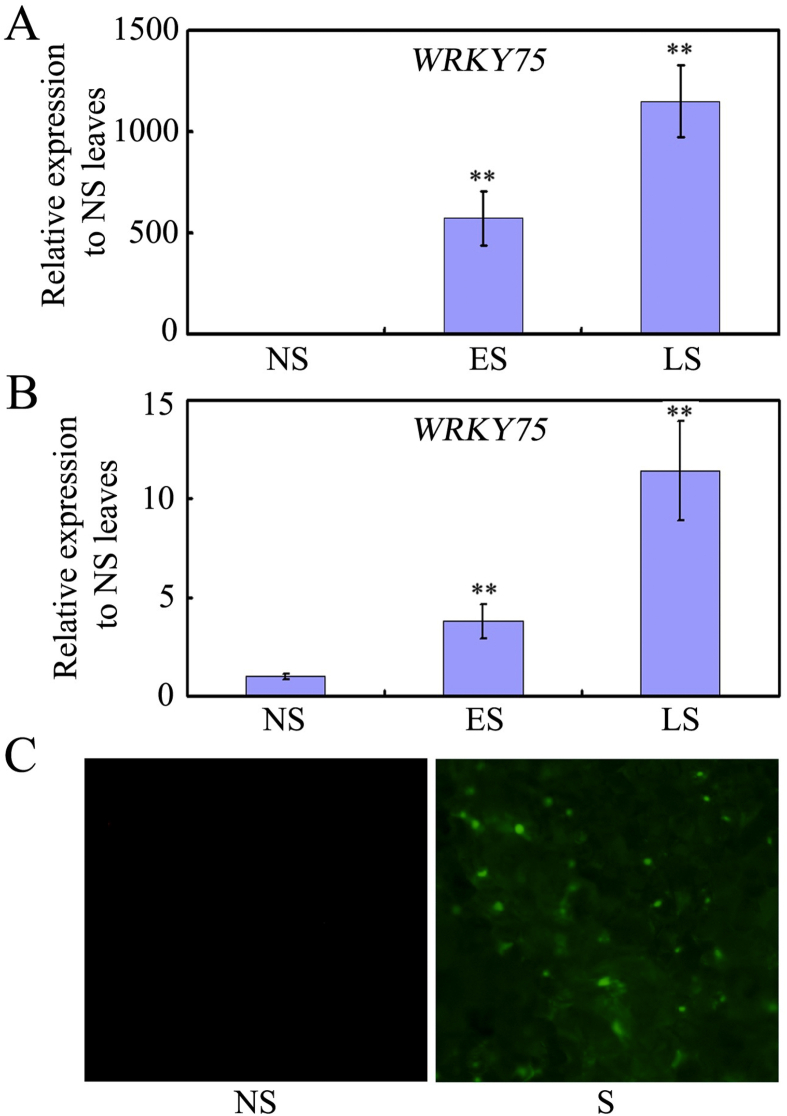
Fig. 1.
Expression of WRKY75 in senescing leaves. (A) qRT-PCR analysis of WRKY75 transcript levels in wild-type leaves at different developmental stages. Transcript levels of WRKY75 in non-senescent (NS) leaves were arbitrarily set to 1. Values are means ± SD of three independent biological replicates. ∗∗P < 0.01, Student's t-test compared with NS leaves. (B) qRT-PCR analysis of WRKY75 transcript levels in different parts of a senescing wild-type leaf. Transcript levels of WRKY75 in NS leaves were arbitrarily set to 1. Values are means ± SD of three independent biological replicates. ∗∗P < 0.01, Student's t-test compared with NS parts of a senescing wild-type leaf. (C) YFP detection of WRKY75 in wrky75-25 mutant background that harbors the WRKY75:YFP-WRKY75:3′-WRKY75. YFP signals were observed in senescing leaves of the WRKY75:YFP-WRKY75:3′-WRKY75 transgenic plants. These experiments were performed three times with similar results.