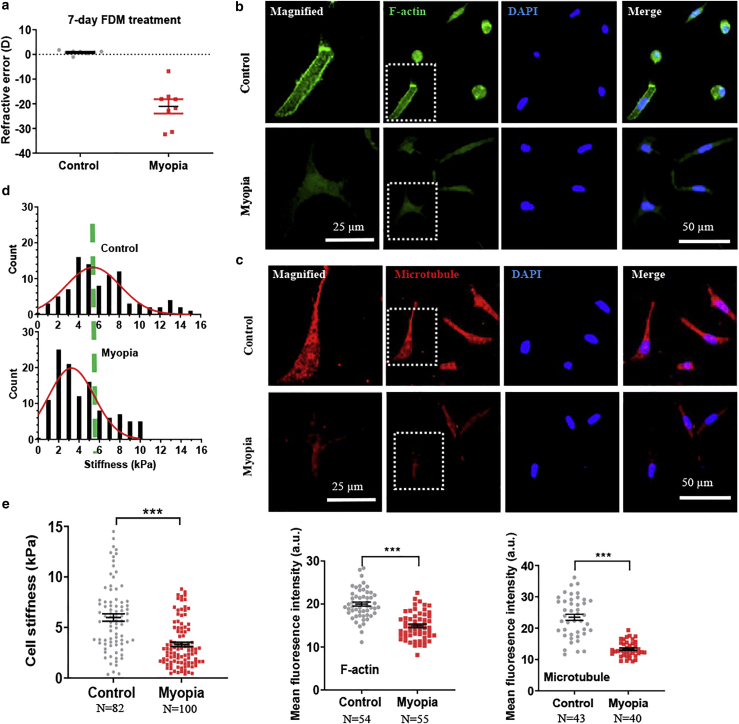
Figure 1.
Myopic corneal cells exhibit reduced F-actin and microtubule and cellular stiffness. (a) Refractive state after the FDM treatment. Representative results of at least three independent experiments are shown. (b and c) Myopic corneal cells exhibit lower levels of F-actin and microtubule than control cells. Single cells were extracted from the treated and fellow untreated control corneas in the FDM model. F-actin and microtubule were stained through immunofluorescence, and the fluorescence intensity was quantified in the bottom panels. The cells in the dotted square were magnified on the left. Scale bars, 50 μm in the nonmagnified images and 25 μm in the magnified images. Representative results of three independent experiments are shown. (d) The histogram of the stiffness of myopic corneal cells and control cells. The stiffness of myopic corneal cells and control cells was measured by AFM. (e) Myopic corneal cells are softer than control cells. n > 80 cells. Representative results of three independent experiments are shown. The number of cell samples was shown in the figures. ∗∗∗p < 0.001. To see this figure in color, go online.