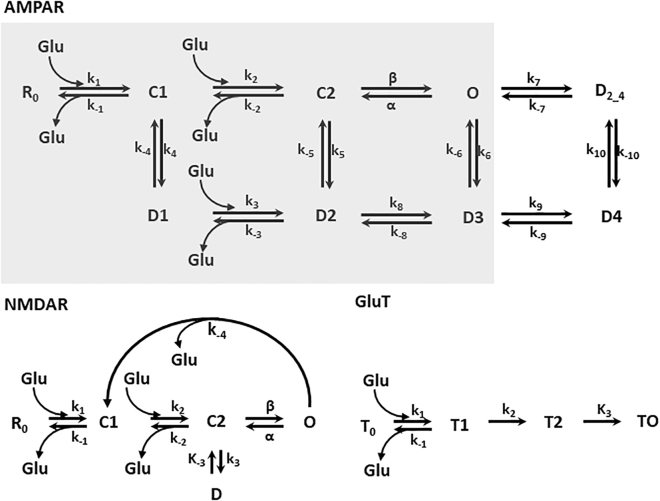
Figure 2.
Kinetic scheme for AMPAR, NMDAR, and glutamate transporters. For AMPAR, the resting state is R0; C1 and C2 are closed states; O is the open state; D1, D2, D3, D4, and D2_4 are desensitized states. k1, k2, β, k3, k4, k5, k6, k7, k8, k9, and k10 are forward rates; k−1, α, k−2, k−3, k−4, k−5, k−6, k−7, k−8, k−9, and k−10 are the backward rates. The three-glutamate binding and dissociation events are shown. The gray box indicates the kinetic scheme utilized in Heine et al. (4). NMDAR, the resting state is R0; C1 and C2 are closed states; O is the open state; D is the desensitized state. k1, k2, β, and k3 are forward rates; k−1, α, k−2, and k−3 are the backward rates. GluT is resting state T0; T1 is glutamate bound facing the synaptic cleft, T2 is glutamate transport away from the synapse, T0 is glutamate dissociation. The value of the rate constant is given in Table 1.