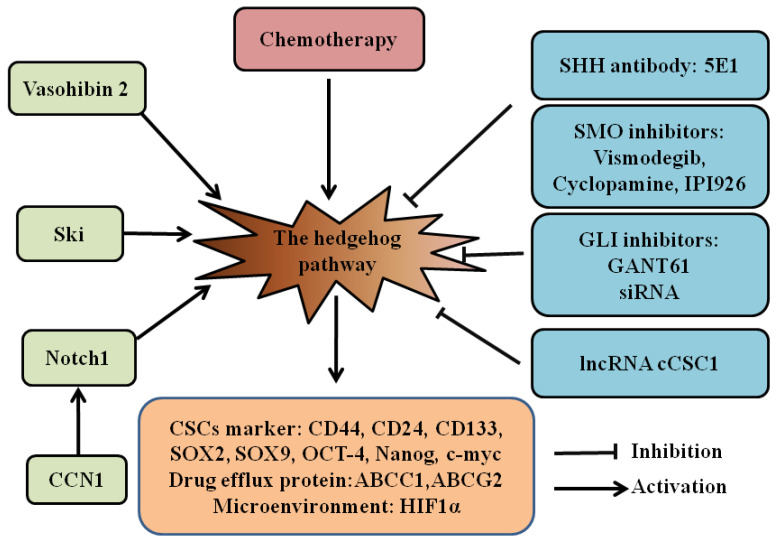
Figure 1.
The HH pathway in gastrointestinal CSCs. The role of the hedgehog pathway in drug resistance of gastrointestinal CSCs and inhibitors for hedgehog signaling is summarized. In gastrointestinal CSCs, CCN1, Notch1, Ski, Vasohibin2, and chemotherapy can activate the HH pathway to increase stemness through upregulating CD44, CD24, CD133, SOX2, SOX9, OCT-4, Nanog, and c-myc, to increase drug resistance by elevating the expression of the drug efflux protein ABCC1 and ABCG2, and to adapt to hypoxia via high expression of HIF1α. The HH inhibitors (5E1, vismodegib, cyclopamine, IPI926, GANT61, GLI siRNA, and lncRNA cCSC1) can attenuate these processes. Hedgehog (HH); cancer stem cells (CSCs); cellular communication network factor 1 (CCN1); ATP-binding cassette subfamily C member 1 (ABCC1); ATP-binding cassette subfamily G member 2 (ABCG2); hypoxia inducible factor 1α (HIF1α).