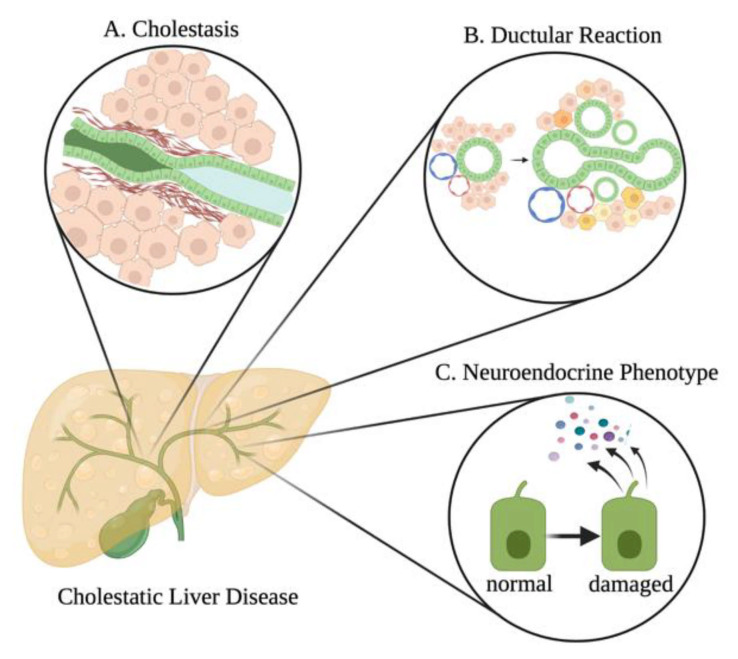
Figure 3.
Histopathology of bile duct damage. Different bile duct damages associated with cholestatic liver diseases. (A) Following bile duct damage, stricturing of the bile ducts can occur from various processes, including significant peribiliary fibrosis. This stricturing can lead to cholestasis (i.e., blockage of drainage of bile from the liver). (B) Cholestatic injury can lead to ductular reaction, which can be accompanied by enhanced biliary inflammation and fibrosis. (C) Following damage, cholangiocytes can enter a neuroendocrine phenotype, whereby they increase their synthesis and secretion of various growth factors, neurohormones, cytokines, chemokines, and other factors that can modulate liver damage through autocrine and paracrine signaling mechanisms. Image made with BioRender (https://biorender.com/).