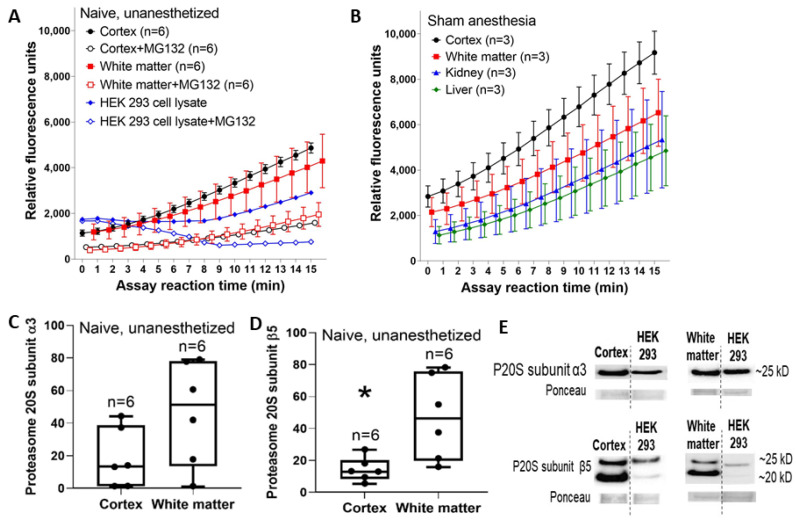
Figure 2.
Reaction progress curves for proteasome activity in somatosensory cortex and subcortical white matter of uninjured neonatal piglets. (A) The proteasome inhibitor MG132 reduced fluorescence in the cortex and white matter independently (p = 0.005) and interactively with assay time (p < 0.001). In post-hoc comparisons, MG132 decreased the fluorescence levels in the cortex (p < 0.001) and white matter (p < 0.001). Proteasome activity did not differ between the cortex and white matter in the presence or absence of MG132 (p > 0.05 for both). An HEK293 cell lysate with and without MG132 treatment is shown for a control comparison. (B) Separate piglets received 3 h of normothermic sham anesthesia and 24-h recovery. The cortex had the highest proteasome activity followed by the white matter. The liver and kidney had lower activity than either brain region. Data are shown as means with standard errors of the means. (C,D) Western blot analysis showed that naïve cortex and white matter had similar proteasome 20S subunit α3 levels (C, p = 0.094), but immunoreactivity for proteasome 20S subunit β5 was higher in white matter than in the cortex (* p = 0.015). Between-gel comparisons were made by dividing each band’s immunoreactivity optical density by the density of a common HEK293 cell lysate that was loaded into every gel. In panels (C,D), each circle represents one piglet and the box plot whiskers are 5–95th percentiles. (E) Representative western blots of the naïve, unanesthetized piglet brain. Bands from the cortex and the HEK293 cell lysate are shown from the same gel with the same exposure time. Separate gels have bands from white matter and the HEK293 cell lysate. Molecular weights are indicated.