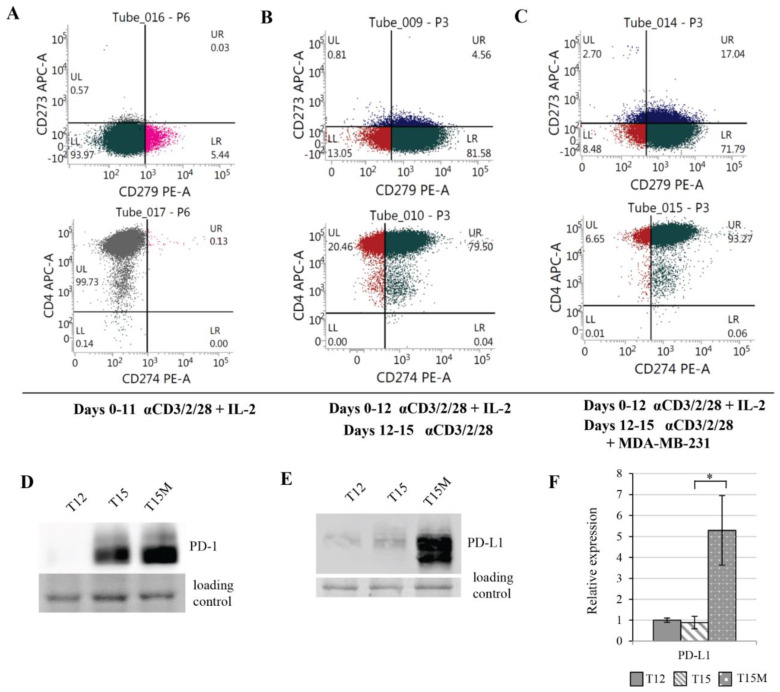
Figure 3.
Prolonged polyclonal stimulation induced the expression of PD-1 (CD279), PD-L1 (CD274), and PD-L2 (CD273) in CD3+CD4+ T cells, which was additionally increased due their exposure to MDA-MB-231 cancer cells. Flow cytometry plots show the expression levels of CD279, CD273, CD274, and CD4 on the surfaces of (A) CD4+ T cells activated with anti-CD3/CD28/CD2 moAb-coated stimulatory beads and expanded in the presence of IL-2 (10 U/mL) for 11 days, (B) CD4+ T cells expanded with anti-CD3/CD28/CD2 Ab-coated stimulatory beads and with IL-2 (10 U/mL) for 12 days, restimulated on day 12 with anti-CD3/CD28/CD2 Abs without exogenous IL-2 and cultured up to day 15 in the absence of cancer cells, or (C) cultured up to day 15 in the presence of MDA-MB-231 cancer cells. (D) The protein levels of PD-1 and (E,F) PD-L1 were highly increased in CD4+ T cells when restimulation of lymphocytes was performed in the presence of MDA-MB-231 cancer cells. (F) The data from 3 independent biological replicates (donors) are presented, the statistical significance of which was calculated using Student’s t-test p < 0.05. Statistically significant values are indicated by asterisks. The uncropped blots and molecular weight markers are shown in Supplementary Materials.