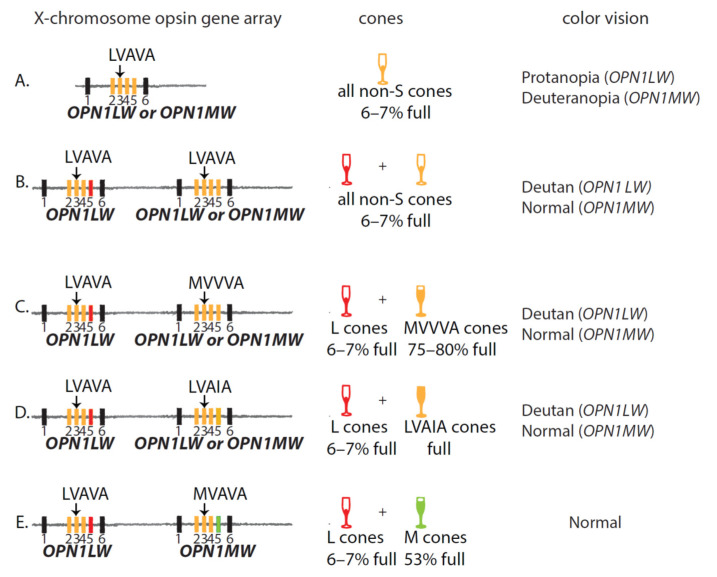
Figure 4.
Opsin gene arrays with LVAVA haplotype and the associated color vision. Rectangles represent exons; see Figure 2 and Figure 3 for a description of the color-coding. For example, the yellow rectangle representing exon 5 indicates the gene may be OPN1LW or OPN1MW. (A) Array with a single opsin gene that is either OPN1LWLVAVA or OPN1MWLVAVA. A male with an array like this will be an obligate deuteranope if the gene is OPN1LW or an obligate protanope if the gene is OPN1MW. Deuteranopes have functional S and L cones; protanopes have function S and M cones. (B) An array in which both expressed positions have the LVAVA haplotype. In a male with this array all non-S cones will have a small amount of functional photopigment. The color vision phenotype depends on whether the second gene is L (deutan) or M (normal). (C,D) An array with OPN1LWLVAVA in the first position and an OPN1LW or OPN1MW gene with the MVVVA (C) or LVAIA (D) haplotype in the second position. Males with one of these arrays will have CVD or normal color vision depending on whether the second gene is OPN1LW (deutan) or OPN1MW (normal). (E) An array with OPN1LWLVAVA and OPN1MWMVAVA. A male with this array will have functional L and M cones and thus normal color vision. Arrays in this figure are based on patients described in Tables S4–S6 [22,31,32,33,38,39,81].