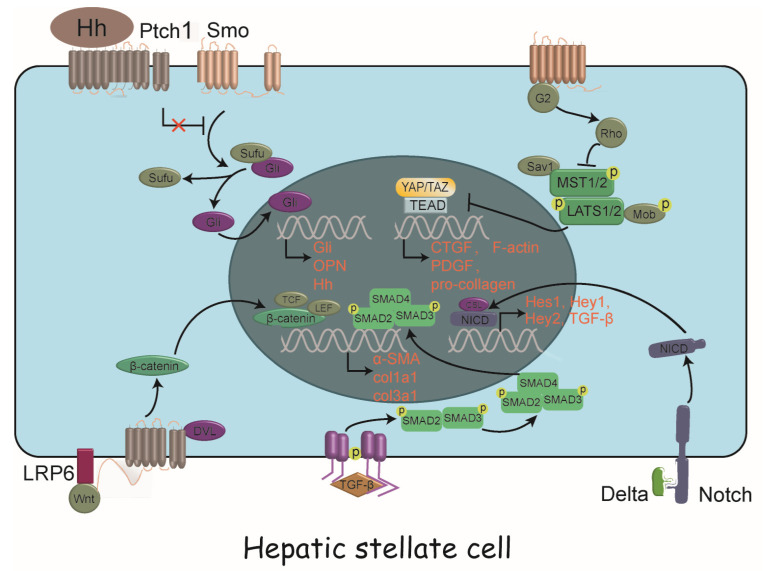
Figure 2.
Intracellular signaling pathways driving HSC activation. A panoply of signals drive HSC activation, including TGF-β/SMAD pathway, Notch signaling, Wnt/β-catenin signaling, Hedgehog signaling and Hippo signaling, with complex crosstalk between them. HSC, hepatic stellate cell; Hh, hedgehog; Ptch1, patched 1; Smo, smoothened; Sufu, suppressor of fused; Gli, glioma-associated oncogene homolog; OPN, osteopontin; TCF, T lymphocyte factor; LEF, lymphocyte enhancer factor; LRP6, low-density lipoprotein receptor 6; DVL, disheveled; SMAD, small mother against decapentaplegic; α-SMA, α-smooth muscle actin; col1a1, collagen I α-1; TGF-β,transforming growth factor β; Sav1, Salvador family WW domain containing protein 1; MST1/2, mammalian STE20-like protein kinase 1 and 2; LATS1/2, large tumor suppressor kinase 1 and 2; Mob, monopolar spindle-one-binder protein; YAP, yes-associated protein; TAZ, transcriptional coactivator with PDZ-binding motif; TEAD, TEA domain transcription factor; CTGF, connective tissue growth factor; PDGF, platelet derived growth factor; NICD, Notch intracellular domain; CSL, CBF-1, Suppressor of hairless, Lag-2; Hes, hairy/enhancer of split ; Hey, hairy/enhancer of split related with YRPW motif.