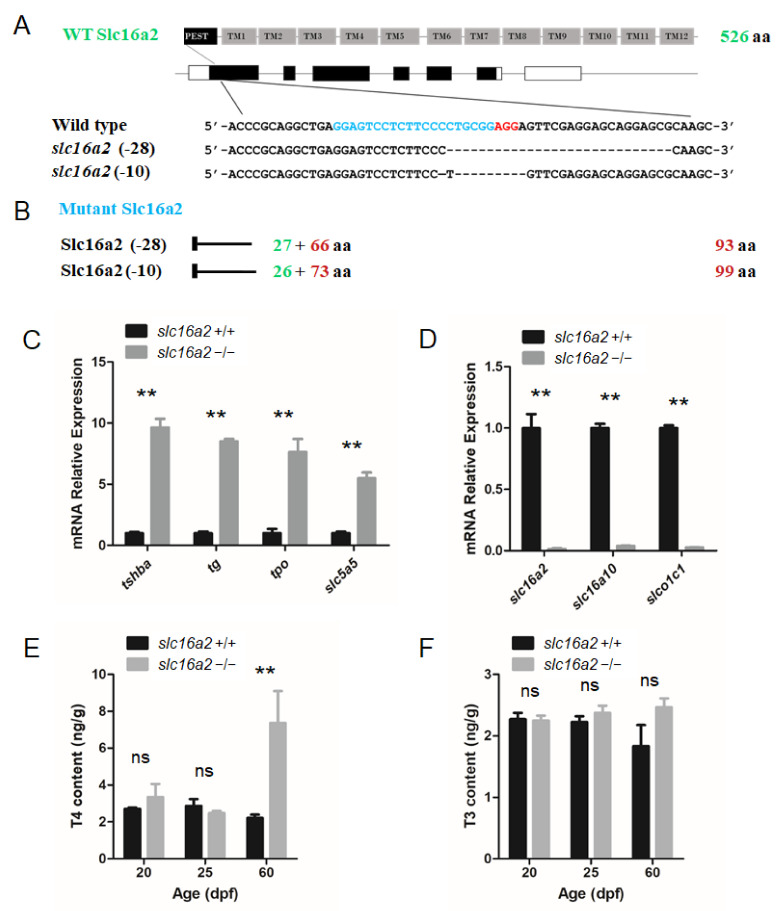
Figure 7.
Generation of the slc16a2 mutant zebrafish. (A) Schematic illustration representing the zebrafish Slc16a2 protein (upper panel) and slc16a2 locus with the CRISPR target site on exon 1 (middle panel). Sequencing of the slc16a2 target CRISPR site in wild type, slc16a2 (-28) mutant, and slc16a2 (-10) mutant zebrafish lines are shown in the lower panel. (B) The predicted truncated Slc16a2 proteins resulting from premature translational termination are shown. (C) Quantitative RT-PCR analyses of tshba, tg, tpo, and slc5a5 expression in slc16a2 mutants and their wild-type siblings at 5 dpf. (D) Quantitative RT-PCR analyses of slc16a2, slc16a10, and slco1c1 expressions in slc16a2 mutants and their wild-type siblings at 5 dpf. (E) Whole-body T4 contents of slc16a2 mutants and their wild-type siblings at 20, 25, and 60 dpf. (F) Whole-body T3 contents of slc16a2 mutants and their wild-type siblings at 20, 25, and 60 dpf. ** p < 0.01, ns: No significance.