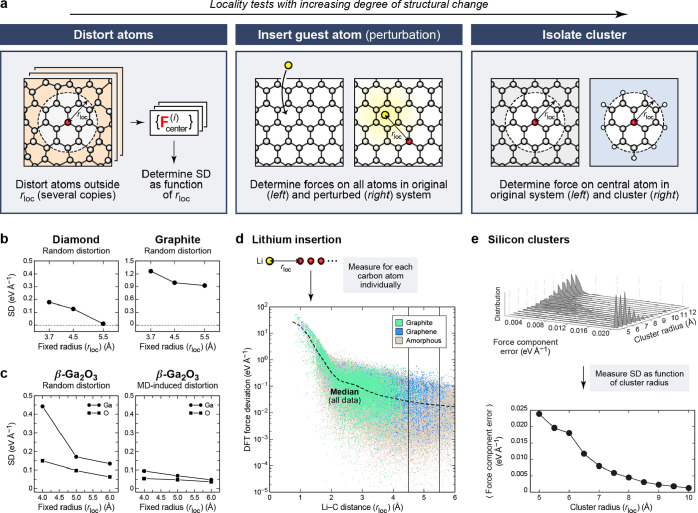
Figure 21.
Protocols for quantifying force locality. (a) Schematics of three approaches that make increasingly drastic changes to the structure up to a characteristic radius, rloc—drawn following ref (122), with the left panel adapted from that work. From left to right: (i) distortions of atoms outside rloc around a central atom, estimating locality by measuring the standard deviation (SD) of the force on this atom as a function of rloc; (ii) insertion of a guest atom, estimating locality by measuring the change in the forces on all atoms depending on their distance from the guest atom, taken to be rloc; (iii) isolation of a cluster fragment with radius rloc, estimating locality by determining the force difference for the central atom between the cluster and the original system. (b) Results of locality tests for diamond and graphite, highlighting qualitatively different behavior: in diamond, the interactions decay quickly, and perturbing atoms more than 5.5 Å away from the center does not substantially influence the force on the central atom. In graphite, on the other hand, there is a high degree of nonlocality. Reprinted with permission from ref (122). Copyright 2017 by the American Physical Society. (c) Same for β-Ga2O3. Two different strategies were used: random distortions, as in the panels above, or MD-induced distortions. Adapted from ref (182). Copyright 2020 AIP Publishing. (d) Force locality in graphitic and other carbon structures, where the perturbation is the addition of a Li atom. Adapted from ref (119). Copyright 2018 AIP Publishing. (e) Force locality in bulk silicon configurations, estimated via the force component differences on the respective central atom between clusters of different radii and the corresponding original structure.183 Republished with permission of IOP Publishing, from ref (183); permission conveyed through Copyright Clearance Center, Inc. © 2005 IOP Publishing. Reproduced with permission. All rights reserved.