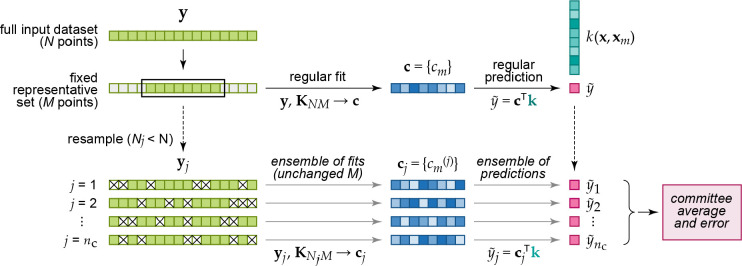
Figure 27.
Schematic of the construction and use of a committee model for uncertainty estimation in sparse GP models, as described in ref (202). Similar graphical representations are used as in Figures 4 and 5: here, multiple models are trained using the same representative set but different random subselections of the training set, yj. The cost of training scales linearly with the number of committee members, nc, and each training yields a different weight vector, cj. When performing a prediction, a single vector of kernels, k, needs to be evaluated (which is usually the computationally intensive task for prediction), and multiple predictions, ỹj, can be obtained cheaply by taking scalar products of k with the individual weight vectors corresponding to the members of the committee. Example applications of this methodology are shown in Figure 28.