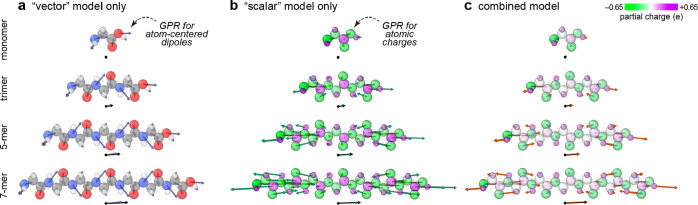
Figure 42.
Learning dipole moments. The figure shows atom-centered contributions to the dipole moment of different polyglycine molecules from the monomer to the 7-mer. (a) Results of a “vector” (λ = 1) SA-GPR model in which the predicted dipole is made up of atom-centered dipoles (gray vectors). (b) Results of a scalar (λ = 0) GPR model, where atom-centered charges (whose magnitude is indicated by the green/purple color scale) are predicted instead and used to calculate the molecular dipole moment. For this model, the green vectors show the predicted charges multiplied by the atomic displacements. (c) Results of a model in which scalar and vector SA-GPR are combined, and the prediction is a combination of atom-centered dipoles and charges (red vectors give the weighted sum of the two contributions). Below each molecule, the black vector gives the molecular dipole moment calculated using the reference electronic-structure method (B3LYP-DFT), and the gray, green, or red vector gives the total GPR prediction. Adapted from ref (392).