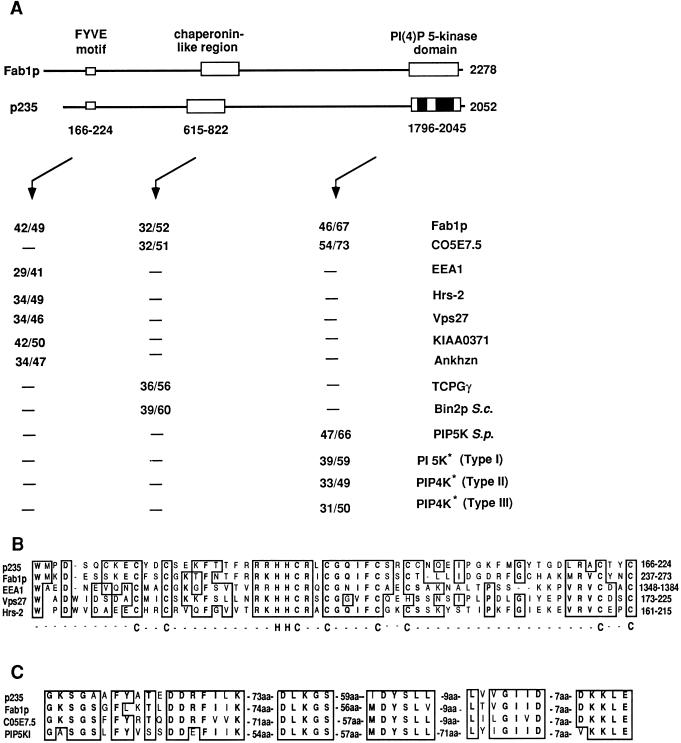
FIG. 2.
Sequence analysis of p235. Similarity of mouse p235 to other FYVE finger-containing proteins, molecular chaperones, PI 5-Ks, and PIP 4-Ks. (A) Map of the domain structure of p235 and of related domains in Fab1p. Values are percentages of identity over percentages of similarity between the indicated proteins, the boxed areas, or the black portions of the PI(4)P5K domain (asterisks). The amino acid sequences used for the analysis were obtained from the following GenBank database accession numbers: S. cerevisiae Fab1p, 398498; C. elegans C05e7.5, 1065686; human EEA1, 2135066; rat Hrs-2, 1885385; S. cerevisiae Vps27, 785067; human KIAA0371, 2224683; mouse Ankhzn, 2914017; human TCP1-γ, 1729873; S. cerevisiae (S.c.) Bin2p, 493574; Schizosaccharomyces pombe (S.p.) PIP 5-K, 2894286; human PI 5-Kα (type I), 1743875; human PIP 4-K (type II), 1346720; and human PIP 4-K (type III, now considered to be type II), 1730569. (B) FYVE finger in a conserved Zn2+-binding region. Potential Zn2+-coordinating His-Cys clusters are indicated below the alignment. (C) Alignment showing similarities between subsets of highly conserved motifs with a predicted role in PI 5-K function. Similarities and identities are denoted by boxed areas. aa, amino acids.