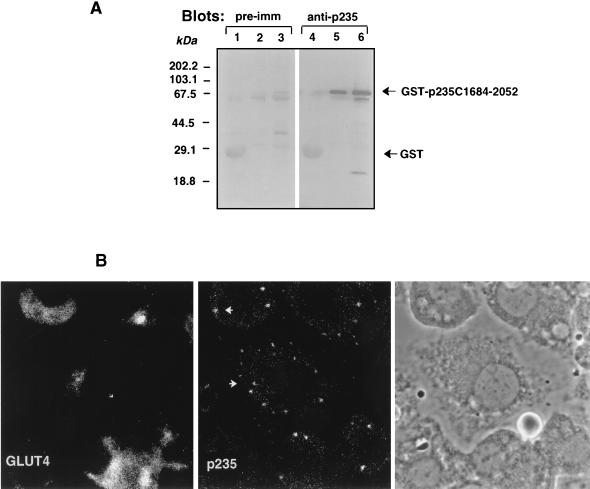
FIG. 6.
Intracellular localization of endogenous p235 in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. (A) Specificities of anti-p235 antibodies. GST or GST–p235-C1684-2052 fusion proteins were expressed in E. coli XA-90 and purified on glutathione-agarose beads as described in Materials and Methods. Aliquots of the beads equivalent to 2 μg of GST (lanes 1 and 4) and 200 and 800 ng of GST–C1684-2052 (lanes 2 and 5 and lanes 3 and 6, respectively) were boiled in Laemmli sample buffer, resolved by SDS-PAGE (10.5% acrylamide; duplicate gels) and analyzed by immunoblotting with preimmune (pre-imm; dilution, 1:500) or anti-p235 (R6953; dilution, 1:3,000) antiserum as indicated. Anti-p235 peptide antiserum, generated against the C-terminal 18 residues (amino acids 2035 to 2052), detects specifically and in a linear relationship the C-terminal p235 protein (lanes 5 and 6). (B) Immunofluorescence microscopy of immunoreactive p235 in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Cells, grown and differentiated on coverslips, were washed, fixed in methanol, permeabilized, and stained with the anti-p235 antibodies affinity purified on a GST–C1684-2052 protein band cut from the nitrocellulose membrane shown in panel A. For the double labeling, mouse monoclonal anti-GLUT4 antibody (1F8) was used. Immunodetection of anti-p235 was achieved with fluorescein isothiocyanate-conjugated goat anti-rabbit IgG, and that of anti-GLUT4 IgG was achieved with Texas red-conjugated goat anti-mouse IgG. The phase-contrast image depicts cell shape and nuclei of the same field.