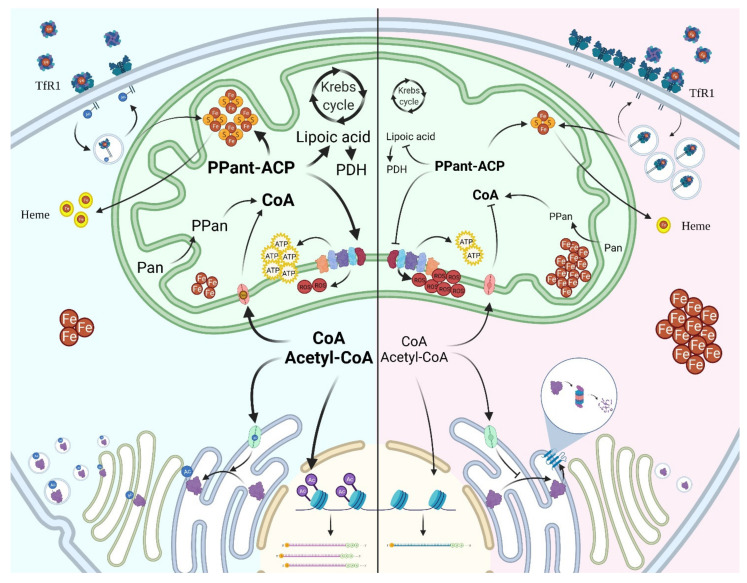
Figure 2.
Schematic overview of the biochemical pathways involving CoA in normal (blue panel) or pathological conditions (red panel). The figure recapitulates some of the numerous intracellular processes requiring CoA or its thioester derivatives and found to be affected in disorders due to inborn errors of CoA biosynthesis or to altered compartmentalization. The important roles in the intermediate metabolism and mitochondrial energy production and in protein post-translational modifications (acetylation of histones and ER resident and transiting proteins, palmitoylation of TfR1, pantetheinylation of ACP) are summarized together with the effects observed in total or organellar CoA deficiency (iron accumulation, increased ROS production, defective energy production, reduced efficiency of protein secretion and ER degradation). Abbreviations: Pan, pantothenate, PPan, phosphopantothenate, PPAnt-ACP, phosphopantetheinyl-Acyl Carrier Protein, PDH, pyruvate dehydrogenase, TfR1, Transferrin Receptor 1.