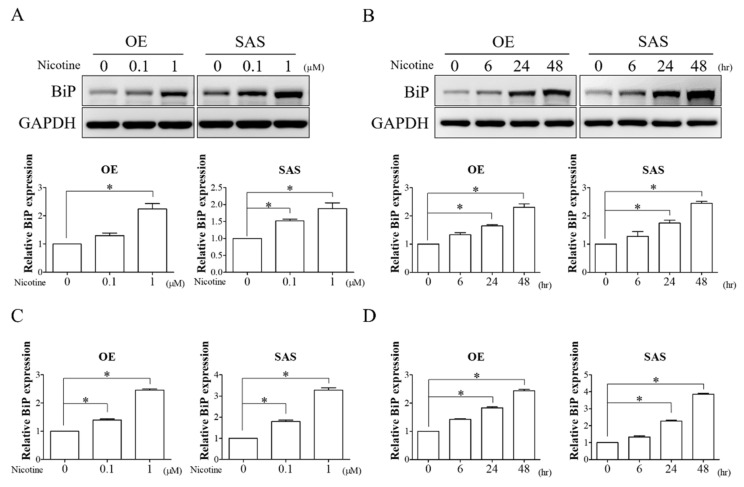
Figure 1.
Nicotine increased BiP expression in a dose- and time-dependent manner. (A,C) OE and SAS cells were treated with 0.1 and 1 μM of nicotine for 48 h. The dose-dependent effect of nicotine on BiP expression was analyzed by Western blot analysis and quantitative RT-PCR. The graphs show the quantification of Western blots (A, lower panels). Band intensities were quantified using ImageJ software. The relative protein expression of BiP was normalized to GAPDH expression. (B,D) OE and SAS cells treated with 1 μM nicotine for 6, 24, and 48 h were subjected to Western blot analysis and quantitative RT-PCR for investigating the time-dependent effect of nicotine on the expression of BiP. The graphs demonstrate the quantification of Western blots (B, lower panels). Band intensities were analyzed using ImageJ software. The relative protein expression of BiP was normalized to GAPDH expression. GAPDH was used as the loading control. * p < 0.05 by one-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni’s post hoc test. Data are presented as the mean ± SEM of three independent experiments. SEM, error bars.