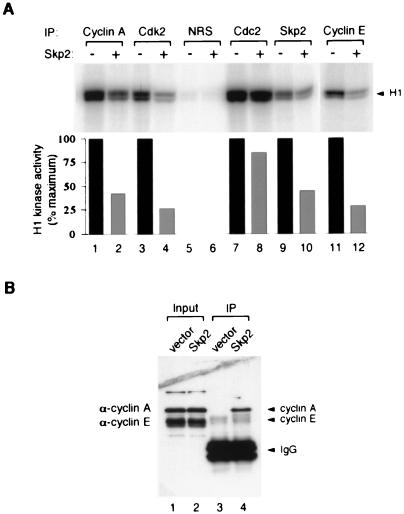
FIG. 5.
Inhibition of endogenous cyclin-CDK kinase activity by Skp2. (A) HeLa cell extracts (250 μg) were immunoprecipitated with antiserum against cyclin A or Cdk2, NRS, or serum against Cdc2, Skp2, or cyclin E, as indicated above the lanes. The immunoprecipitates were incubated with buffer (odd-numbered lanes) or 1 μg of bacterially expressed Skp2-H6 (even-numbered lanes) at 30°C for 30 min. The kinase activity against histone H1 was then assayed, and phosphorylation was analyzed by SDS-PAGE (17.5% gel) followed by phosphorimagery. Quantitation of histone H1 phosphorylation from the phosphorimagery is shown in the lower panel; the kinase activity associated with NRS immunoprecipitates in lanes 5 and 6 were very low, and the quantitation is not shown. (B) Binding of cyclin A and cyclin E to Skp2. HeLa cells were transiently transfected with a control vector (lanes 1 and 3) or plasmid expressing FLAG-Skp2 (lanes 2 and 4). Extracts were prepared; 200 μg was immunoprecipitated (IP) with anti-FLAG antiserum and dissolved in 30 μl of SDS sample buffer; 10 μl was loaded onto an SDS–17.5% polyacrylamide gel, transferred onto a membrane, and immunoblotted with the anti-cyclin A monoclonal antibody E72 and anti-cyclin E monoclonal antibody HE12.