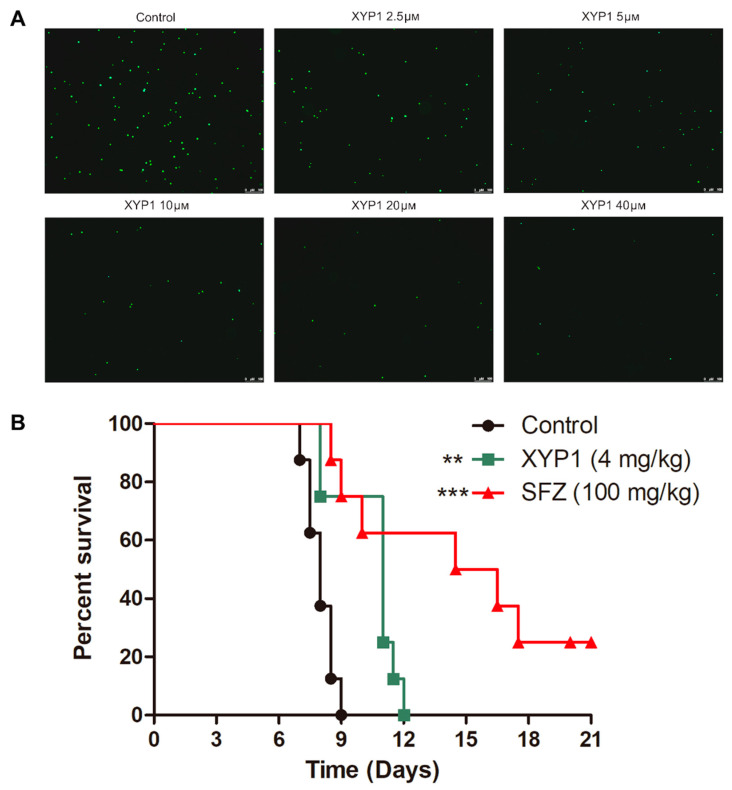
Figure 2.
Anti-T. gondii effects of XYP1 in vitro and in vivo. (A) Viability assessment of T. gondii tachyzoites evaluated by fluorescence microscope. RH-GFP of tachyzoites were treated with different concentrations of XYP1 or DMEM alone (control) for 2 h. The fluorescence intensity was observed using a fluorescence microscope. Scale bars = 100 μm. (B) Effect of XYP1 and SFZ on the survival rate of infected mice. RH 2F strain tachyzoites. Beginning on the day of infection, XYP1 at 4 mg/kg, vehicle (PBS) or positive drug (SFZ) at 100 mg/kg was intraperitoneally administered for 7 days. These mice were observed for an additional 14 days, and the survival times of the infected mice were recorded for 21 days (n = 8 for each group). A log-rank test demonstrated that SFZ and XYP1 statistically prolonged the survival time of infected mice compared with the vehicle group (*** p < 0.0001, ** p < 0.01).