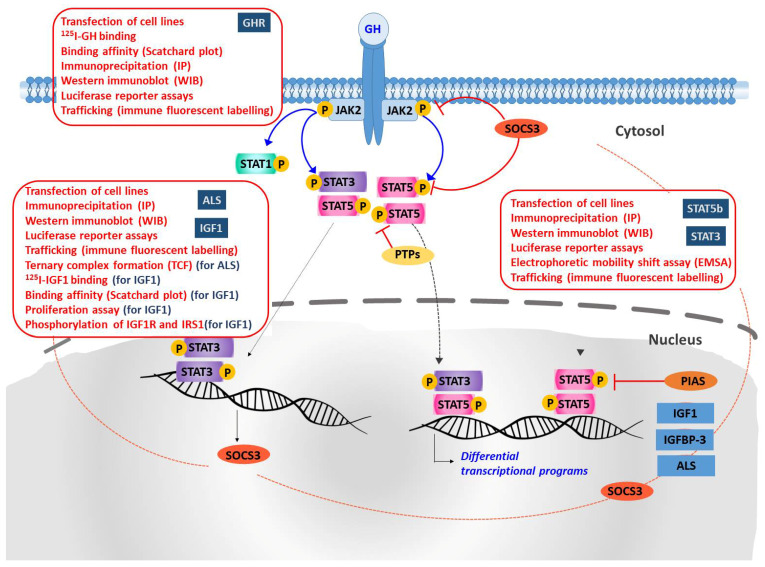
Figure 4.
Schematic representation of GH action and the methodological tools applied to the characterization of genetic variants identified in different molecular players. Upon GH binding to dimerized cell-surface GH receptor (GHR), JAK2 is activated and phosphorylates specific tyrosine residues in the intracellular domain of the receptor. STAT proteins bind to these phosphotyrosine motifs through their SH2 domain, become phosphorylated (STAT-P), form homo and heterodimers, and translocate to the nucleus. In the nucleus, STATs dimers bind to specific promoter elements and regulate gene expression. Expression of insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF1), insulin-like growth factor binding protein-3 (IGFBP-3), and acid-labile subunit (ALS) are upregulated by STAT5 homodimers. Negative regulation of STATs activation is mediated by SOCS (suppressors of cytokine signaling), PIAS (protein inhibitors of activated STATs) and PTPs (protein tyrosine phosphatases).