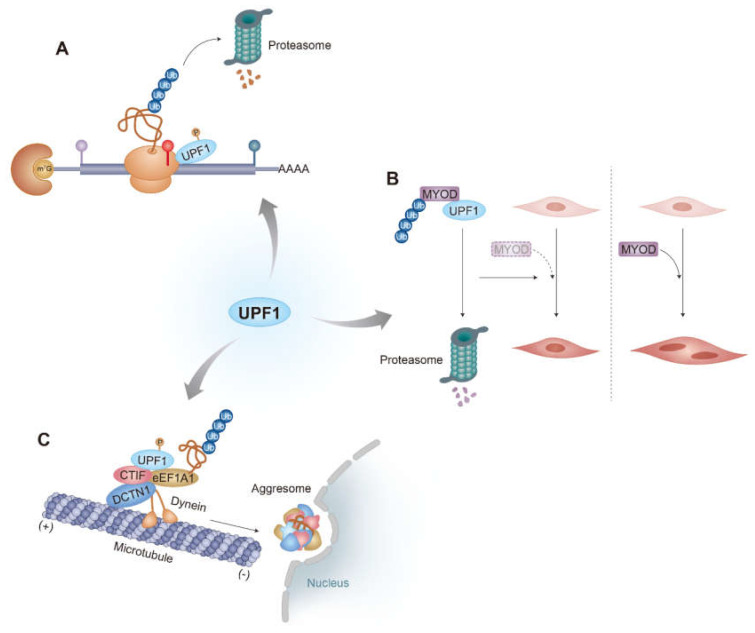
Figure 3.
Diverse functions of UPF1 in protein quality control. (A) UPF1-driven degradation of PTC-polypeptides synthesized during NMD in yeast. Given its coupling to NMD, this function might be dependent on UPF1 hyperphosphorylation. The involvement of the E3 ligase ability of UPF1 and whether this mechanism works for PTC-polypeptides generated in mammalian cells remain to be determined. (B) UPF1-mediated degradation of properly folded proteins via the UPS. The E3 ligase activity of UPF1 is involved in ubiquitination of target proteins. A possible role of UPF1 hyperphosphorylation in this mode of protein degradation should be investigated. (C) UPF1-mediated degradation of misfolded polypeptides via the aggresome-autophagy pathway. UPF1 associates with the CED complex and misfolded polypeptides, ensuring their proper delivery to aggresomes. This mode of protein degradation is dependent on UPF1 hyperphosphorylation, but not on its E3 ligase activity.