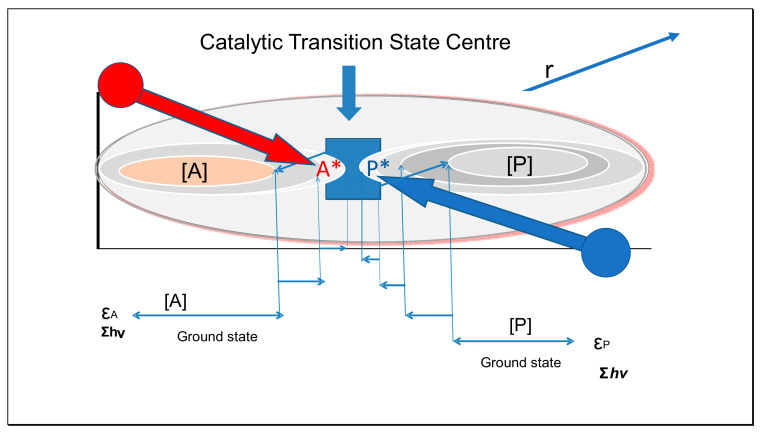
Figure 4.
Radial action transition states on a Brownian catalyst, proposed to generate activation energy for reversible reactions A ↔ P by forceful (δmvr) inertial collisions. Concentrations of A* and P* of similar chemical potential to bulk reactants A and P stabilise in potential wells, binding loosely. At constant temperature, the difference in ground-state energy εPo − εAo represents the enthalpy and chemical potential changes for the reaction.