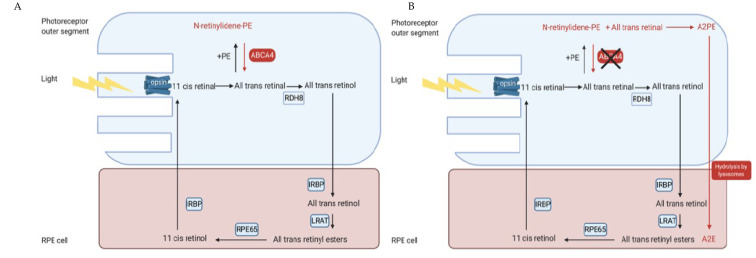
Figure 3.
Schematic diagram illustrating the visual cycle in the photoreceptor outer segments and the RPE. (A) Light photobleaches the opsin and isomerises the 11-cis-retinal to ATR. Some ATR reversibly reacts with PE to form NrPE, which is flipped onto the cytoplasmic side by the ABCA4 protein. The NrPE is then hydrolysed to PE and ATR, thus preventing the accumulation of ATR on the luminal side. The ATR is then reduced to all-trans-retinol by RDH8 and then transported to the RPE cell by IRBP. In the RPE, the all-trans-retinol is esterified to all-trans-retinyl esters by LRAT, which is then converted to 11-cis-retinol by RPE65 isomerohydrolase and then oxidized to 11-cis-retinal by RDH and transported back to the photoreceptors by IRBP. (B) Schematic diagram illustrating the visual cycle in the presence of ABCA4 dysfunction. Dysfunction of the ABCA4 protein prevents the flipping of the NrPE from the luminal side to the cytoplasmic side of the photoreceptor outer segments, meaning that the NrPE accumulates and condenses with all-trans-retinal into A2PE. The photoreceptor outer segments are then shed and phagocytosed by the RPE cell, which then hydrolyse the A2PE to A2E [56]. Created with BioRender.com (accessed on 1 June 2021). Abbreviations: ATR: All-trans-retinal; A2E: N-retinyl-N-retinylidene ethanolamine; A2PE phosphatidyl-pyridinium bisretinoid; IRBP: inter photoreceptor binding protein; LRAT: lecithin retinol acyltransferase, NrPE: N-retinylidene phosphatidylethanolamine; PE: phosphatidylethanolamine; RDH8: retinol dehydrogenase 8; RPE: retinal pigment epithelial.