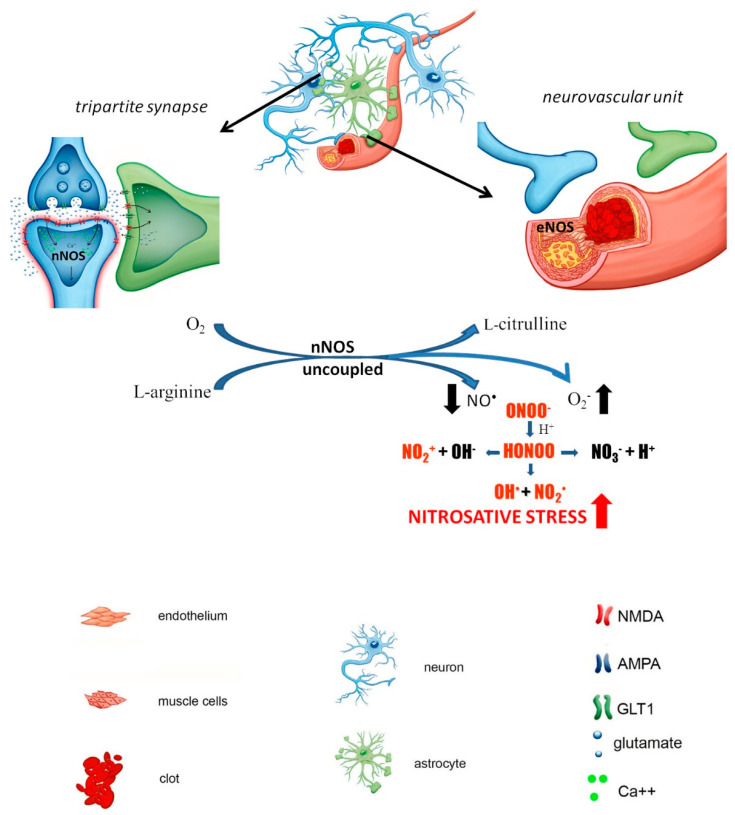
Figure 2.
Early stage of the ischemia (early neuronal damage (0–6 h after ischemic episode): when the clot is formed due to atherosclerotic plaque, under restriction of oxygen supply, the glutamate released by presynaptic neuron accumulates in the synaptic cleft due to reversed activity of GLT1 transporter in the astrocyte; this leads to overactivation of postsynaptic neuron, overactivation of voltage-dependent calcium channels and Ca2+ influx into postsynaptic neuron, that leads to overactivation of nNOS and its uncoupling, and accumulation of ROS/RNS, instead of cGMP.