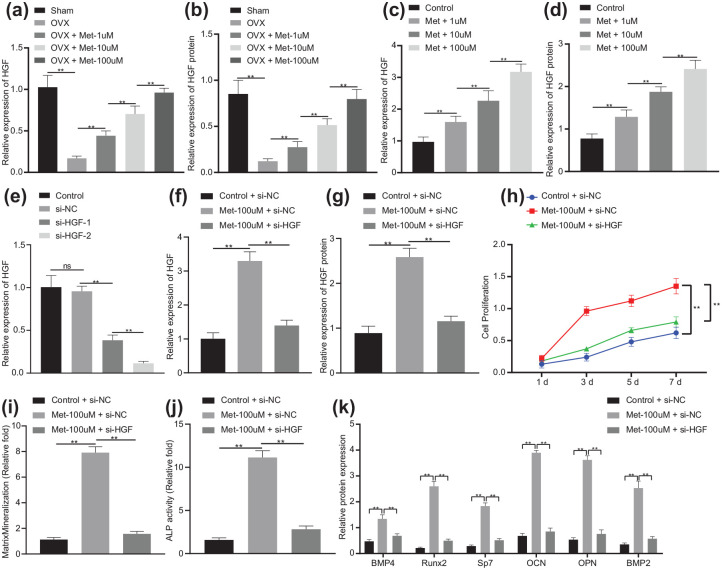
Figure 3.
Melatonin facilitates the differentiation of BMSCs into osteoblasts via HGF upregulation in BMSCs.
(a) mRNA expression of HGF in the femur of OVX or OVX mice treated with melatonin at different concentrations determined by RT-qPCR (n = 10). (b) Western blot analysis of HGF protein expression in the femur of OVX or OVX mice treated with melatonin at different concentrations (n = 10). (c) mRNA expression of HGF in BMSCs treated with melatonin at different concentrations determined by RT-qPCR. (d) Western blot analysis of HGF protein expression in BMSCs treated with melatonin at different concentrations. (e) Silencing efficiency of HGF in BMSCs confirmed by RT-qPCR. (f) mRNA expression of HGF in BMSCs treated with Met-100 μmol/l or in combination with si-HGF determined by RT-qPCR. (g) Western blot analysis of HGF protein expression in BMSCs treated with Met-100 μmol/l or in combination with si-HGF. (h) Proliferation of BMSCs treated with Met-100 μmol/l or in combination with si-HGF measured by CCK-8 assay. (i) Mineralization of BMSCs treated with Met-100 μmol/l or in combination with si-HGF evaluated by ARS staining. (j) Calcification of BMSCs treated with Met-100 μmol/l or in combination with si-HGF evaluated by ALP activity and staining. (k) Western blot analysis of BMP4, Runx2, Sp7, OCN, OPN and BMP2 protein expression in BMSCs treated with Met-100 μmol/l or in combination with si-HGF.
**p < 0.01, indicates statistical significance. Data (mean ± standard deviation) among multiple groups were compared by one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s test while those at different time points were compared by two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni’s correction. Cell experiments were conducted in triplicate.
ALP, alkaline phosphatase; ANOVA, analysis of variance; ARS, alizarin red S; BMSCs, bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells; Met, melatonin; mRNA, messenger ribonucleic acid; OVX, ovariectomy; RT-qPCR, real-time qualitative polymerase chain reaction; si-, small interfering.