Figure 7.
Melatonin delays bone loss and relieves osteoporosis in OVX mice via the HGF/PTEN/Wnt/β-catenin axis.
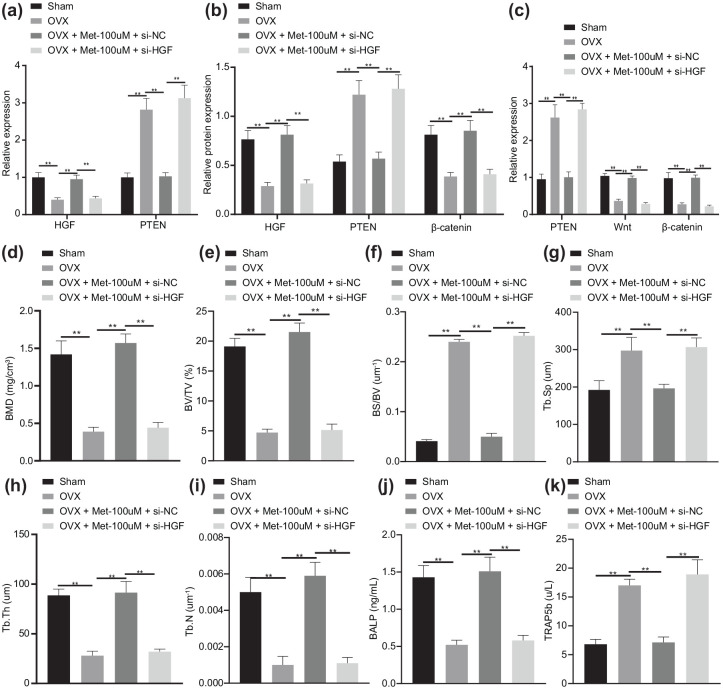
OVX mice were treated with Met-100 μmol/l or in combination with si-HGF. (a) mRNA expression of HGF and PTEN determined by RT-qPCR. (b) Western blot analysis of HGF, PTEN and β-catenin protein expression in OVX mice. (c) Immunohistochemistry analysis of HGF, PTEN and β-catenin proteins. (d) Micro-CT quantitative analysis of BMD in mouse femur. (e) Micro-CT quantitative analysis of BV/TV ratio in mouse femur. (f) Micro-CT quantitative analysis of BS/BV ratio in mouse femur. (g) Micro-CT quantitative analysis of Tb.Sp in mouse femur. (h) Micro-CT quantitative analysis of Tb.Th in mouse femur. (i) Micro-CT quantitative analysis of Tb.N in mouse femur. (j) Serum levels of BALP measured by ELISA. (k) Serum levels of TRAP5b measured by ELISA. **p < 0.01, indicates statistical significance. Data (mean ± standard deviation) among multiple groups were compared by one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s test. n = 10 for mice following each treatment.
ANOVA, analysis of variance; ARS, alizarin red S; BALP, bone-specific alkaline phosphatase; BMD, bone mineral density; BMSCs, bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells; BS, bone surface; BV, bone volume; Ca, calcium; CCK, cell-counting kit; CT, computed tomography; Dpd, deoxypridinoline; ELISA, enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay; Met, melatonin; mRNA, messenger ribonucleic acid; OVX, ovariectomy; P, phosphorus; RT-qPCR, real-time qualitative polymerase chain reaction; si-, small interfering; Tb.N, trabecular number; Tb.Sp, trabecular separation; Tb.Th, trabecular thickness; TV, tissue volume.