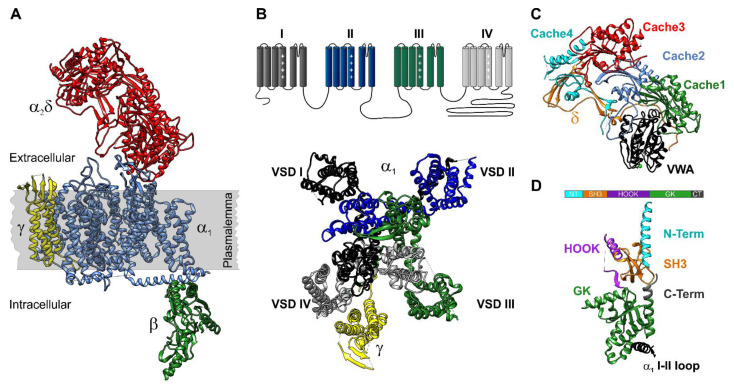
Figure 1.
Structure of the HVCC complex. (A). The HVCC complex consists of the transmembrane, pore-forming α1 and auxiliary intracellular β, extracellular α2δ and transmembrane γ subunits (PDB access code 5GJV [36]). (B). The α1 subunit is formed by four homologous repeats with six transmembrane domains each. The S1 to S4 segments of each repeat form the voltage sensing domain (VSD). S4 carrying four to five positively charged amino acids lysine or arginine serve as actual voltage sensors. The S5 and S6 segments of each repeat form the channel pore. The transmembrane γ subunit interacts with the fourth VSD. (C). The extracellular α2δ subunit consists of four Cache and one von Willebrand factor A (VWA) domain. The VWA domain contains the MIDAS motif (metal ion adhesion site) that coordinates a metal ion (Ca2+) together with residues in the extracellular linker between S1 and S2 segments of the first VSD. (D). Topology of the β2a subunit in complex with the CaV1.2-AID (α interaction domain) located in the intracellular loop between repeats I and II (PDB access code 5V2P [43]). The β subunits are organized in 5 regions: N-terminus, the SH3 domain, HOOK region, and the GK domain.