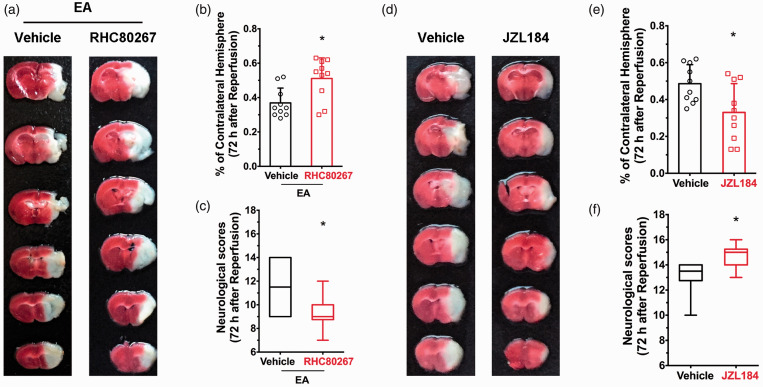
Figure 1.
2-AG mediates EA-induced neuroprotection. (a) Representative images showing infarct tissue following pretreatment with RHC80687 and vehicle. (b,c) EA-induced neuroprotection was abolished by pretreatment of RHC80687 with increased infarct volume (b) and lower neurological scores (c) compared with the vehicle group, induced by focal cerebral ischemia for 60 min. (d) Representative images showing infarct tissue following pretreatment with JZL184 and vehicle. (e,f) JZL184 pretreatment protected the ischemic penumbra from 60 min focal cerebral ischemia with smaller infarct volume (e) and higher neurological scores (f). Infarct volume graphs show mean ± SD; n = 10 mice/group. *p < 0.05 vs. vehicle or wild-type littermates, t-test ((b): p = 0.016; (e): p = 0.019). Neurological behavioral scores show median (range) values; group differences tested using the Kruskal–Wallis test followed by the Mann–Whitney U test. *p < 0.05 vs. vehicle, U test ((c): p = 0.0013; (f): p = 0.019).