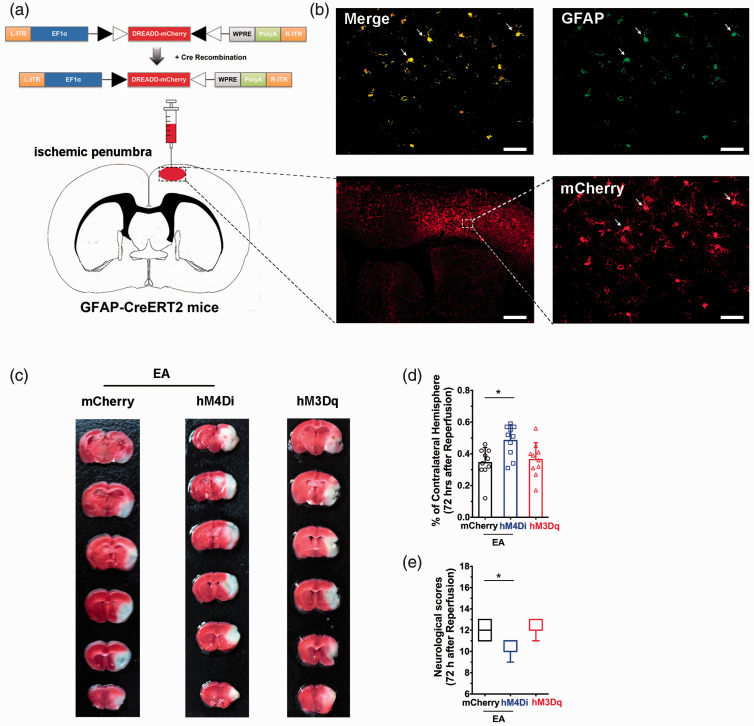
Figure 4.
Ischemic penumbral astrocytes mediate the neuroprotective effects of EA pretreatment. (a) Schematic showing intra-ischemic penumbra injection of DREADD virus in GFAP-Cre mice. (b) Coronal brain section shows the scope with red (mCherry) fluorescence in the right ischemic penumbra after microinjection of different viruses. (c–e) corresponding magnified images (40×) of the box in (b) showing mCherry (red), GFAP, and merge (yellow). Scale bars = 50 µm. (c) Representative images comparing infarct volume in mCherry, hM4Di, and hM3Dq groups. (d,e) Activation of ischemic penumbral astrocytes decreased infarct volume (d) and improved neurological scores (e) induced by focal cerebral ischemia for 60 min. By contrast, inhibition of ischemic penumbral astrocytes decreased infarct volume (d) and decreased neurological scores (e) after EA pretreatment. Infarct volume graphs show means ± SD, n = 10 mice/group, *p < 0.05 vs. mCherry group, one-way ANOVA ((d): p = 0.0023; hM4Di vs mCherry; p > 0.999; hM3Dq vs. mCherry). Neurological behavioral score graphs show median (range) values; group differences were tested with the Kruskal–Wallis test followed by the Mann–Whitney U test. *p < 0.05 vs. mCherry group, U test ((e): p = 0.0092; hM4Di vs. mCherry; p > 0.999; hM3Dq vs. mCherry).