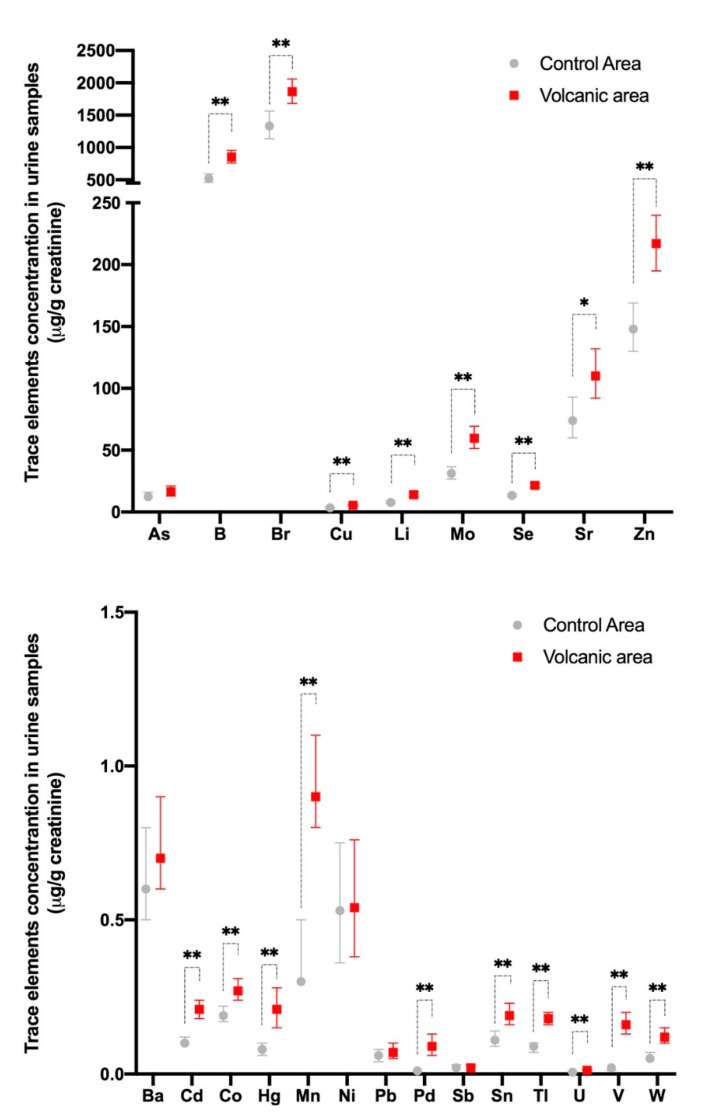
Figure 1.
Metal concentrations in the urine of residents of the Mt. Etna volcanic and the control areas in Sicily. Twenty-three metals and metalloids were measured in the urine of 140 randomly selected permanent residents (F = 67.9%, mean age 48.1 ± 16.7 years) of the Mt. Etna volcanic area and 138 residents (F = 66.7%, mean age 46.3 ± 17.1 years) of adjacent non-volcanic control areas. Metal measurements were performed using an inductively coupled mass spectrometer and are expressed as µg/g creatinine. The values were not normally distributed and therefore the geometric mean was calculated for each specimen, and the values in each group were averaged to determine the mean value and its 95% confidence interval. There were statistically significant differences between the two groups based on linear regression analysis including the log-transformed values of each chemical. For all elements except As, Ba, Ni, Pb, and Sb, the values were significantly higher (* p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01) in the urine of volcanic area residents. Represented data are derived from ref. [25].