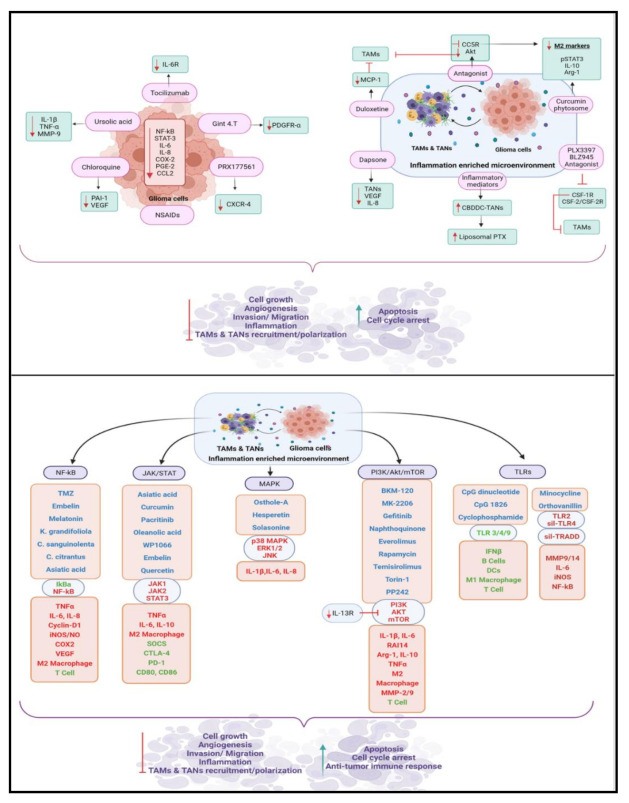
Figure 3.
Represents the therapeutic benefits of targeting inflammatory mediators, TAMs, TANs, and signaling pathways in glioma. Red color indicates inhibition/blocking and green color shows activation/upregulation. NF-κB: Nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells; JAK/STAT: Janus kinase-signal transducer and activator of transcription; MAPK: Mitogen-activated protein kinase; PI3K/Akt/mTOR: Phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase-mammalian target of rapamycin; TLRs: Toll-like receptors; TAMs: tumor-associated macrophages; TANs: tumor-associated neutrophils; IL-1β, -6, -8, -10: interleukins-1β, -6, -8, -10; IL-6R: interleukin-6 receptor; TNF- α: tumor necrosis factor- α; MMP-2/9/14: matrix metalloproteinase-2/9/14; PDGFR-α: platelet-derived growth factor receptor-α; COX-2: cyclooxygenase-2; PGE2: prostaglandin E2; PAI-1: plasminogen activator inhibitor-1; VEGF: vascular endothelial growth factor; NSAIDs: non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs; CXCR-4: chemokine receptor type 4; STAT 3: signal transducer and activator of transcription 3; CCL2: chemokine ligand 2; MCP-1: monocyte chemoattractant protein 1; CC5R: chemokine receptor type 5; CBDDC-TANs: cell-based drug delivery carrier—tumor-associated neutrophils; PTX: paclitaxel; pSTAT3: phosphorylated signal transducer and activator of transcription 3; Arg-1: arginase-1; CSF: colony stimulating factor; Akt/PKB: protein kinase B; TMZ: temozolomide; iNOS: inducible nitric oxide synthase; NO: nitric oxide; T cell: T lymphocyte; SOCS: suppressors of cytokine signaling; CTLA-4: cytotoxic T lymphocyte associated protein-4; PD-1: programmed cell death protein-1; CD80/86: cluster of differentiation 80/86; ERK 1/2: extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2; JNK: c-Jun N-terminal kinase; RAI14: retinoic acid-induced 14 protein; IFN β: interferon β; B cells: B lymphocytes; DCs: dendritic cells; sil-TRADD: silencing TNF receptor type 1-associated DEATH domain protein; sil-TLR4: silencing Toll-like receptor 4.