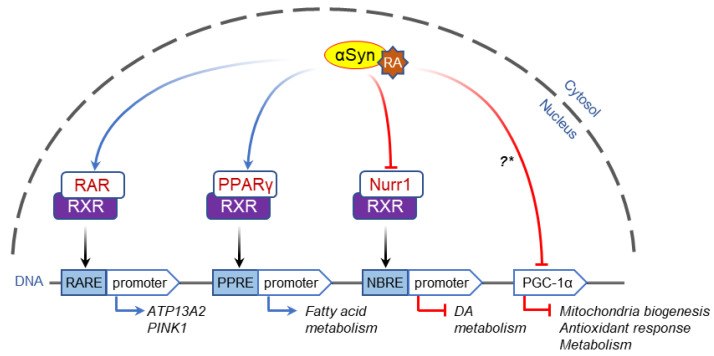
Figure 2.
Effects of α-Syn on transcription factors. Left, α-Syn is translocated to the nucleus in a complex with retinoic acid (RA) where it interacts with and activates RAR and PPARγ nuclear receptors, followed by activation of their corresponding response elements on gene promoter regions. Middle, overexpression of α-Syn also induces downregulation of the orphan nuclear receptor Nurr1, decreasing expression of Death Receptor 5 dependent genes, including those involved in dopamine biosynthesis (TH, AADC, GCH1). Right, α-Syn binds the promoter region of PPARγ co-activator (PGC-1α) gene when overexpressed. This leads to the downregulation of PGC-1α transcription thus reducing cellular protection against oxidative stress and bioenergetic burden. *—It is currently unknown if the interaction with PGC-1α is RA-dependent.