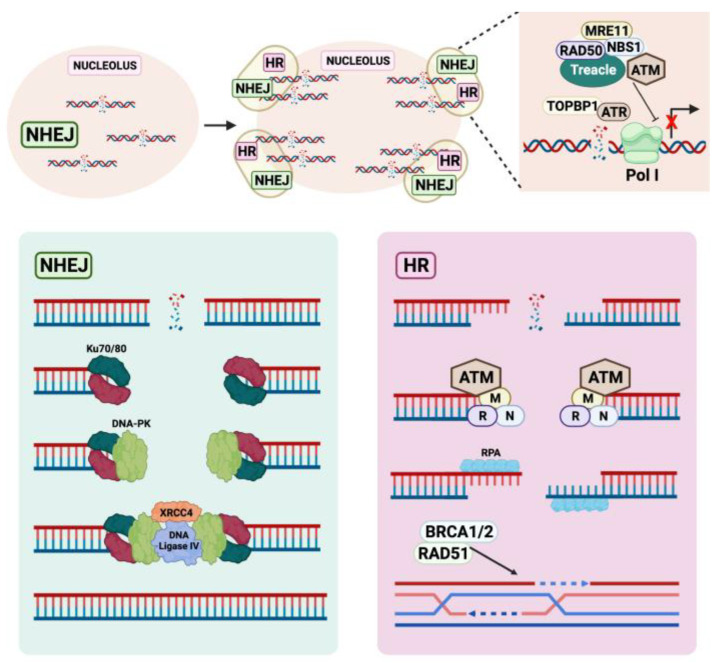
Figure 3.
Mechanism of rDNA repair in the nucleolus. Low levels of rDNA damage are typically repaired via the highly mutagenic NHEJ process. It involves direct ligation of broken ends, mediated by several factors including Ku70/80 heterodimer, DNA-PK, DNA ligase IV and XRCC4 complex. Persistent rDNA damage results in ATM-mediated response that involves Treacle, the MRN complex, TOPBP1 and ATR. This leads to Pol I transcription inhibition and translocation to nucleolar caps, where HR repair occurs. HR proteins RPA, RAD51, RAD52, BRCA1 and BRCA2 are present in abundance in the nucleolar caps. Abbreviations: non-homologous end-joining (NHEJ), DNA-dependent protein kinase catalytic subunit (DNA-PK), X-ray repair cross-complementing protein 4 (XRCC4), homologous recombination (HR), ataxia telangiectasia mutated (ATM), ataxia telangiectasia and Rad3-related (ATR), DNA topoisomerase II binding protein 1 (TOPBP1), RNA Polymerase I (Pol I), replication protein A (RPA), breast cancer susceptibility protein 1 and 2 (BRCA1/2).