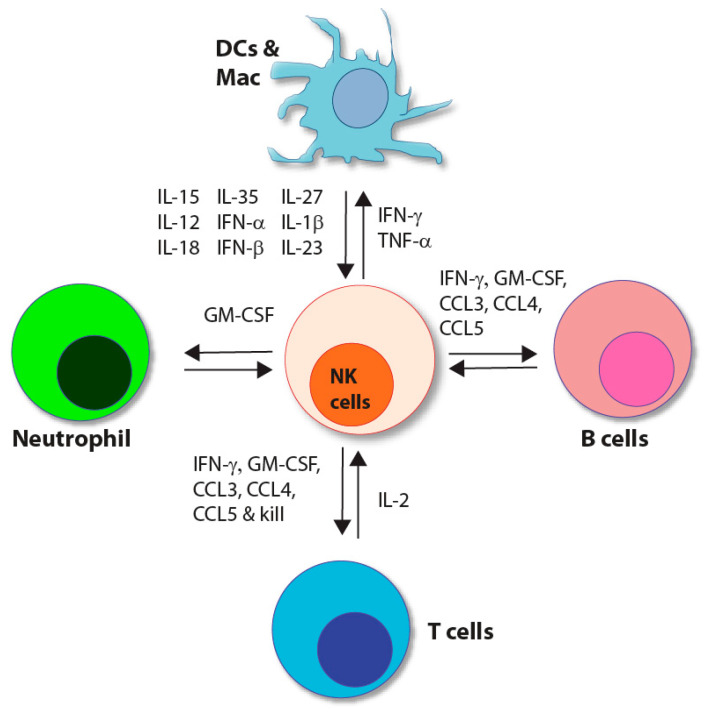
Figure 1.
Bi-directional interaction of NK cells with other immune cells. A brief representation of NK cells’ significant interactions and the innate (myeloid-derived) and adaptive (T and B cell) immune system. Myeloid-derived cells (dendritic cells, macrophages, and neutrophils) secrete various cytokines and chemokines, regulating NK cell effector functions. NK cells secrete cytokines and chemokines (IFN-γ, TNF-a, GM-CSF, CCL-3, CCL-4, and CCL-5) to regulate lymphoid-derived cells (T and B cells).