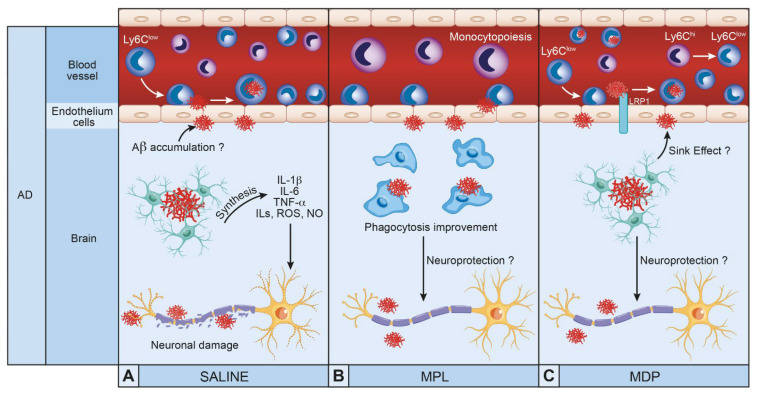
Figure 2.
Therapeutic molecules modulating innate immune cells in Alzheimer’s disease (AD): (A) Accumulation of amyloid beta (Aβ) in the brain over-activates microglia and induces the synthesis of inflammatory cytokines (IL-1β, IL-6, TNF-α, ROS and NO) implicated in neuroinflammation and neuronal damage. (B) Injections of monophosphryl lipid A (MPL) polarize microglia into a neuroprotective aspect and improve microglia phagocytosis toward Aβ. (C) Injection of muramyl dipeptide (MDP) convert inflammatory monocytes (Ly6Chi) into an anti-inflammatory aspect (Ly6Clow) with crawling phenotype. LRP1 transports amyloid through endothelial cells to the luminal side where patrolling monocytes can remove amyloid.