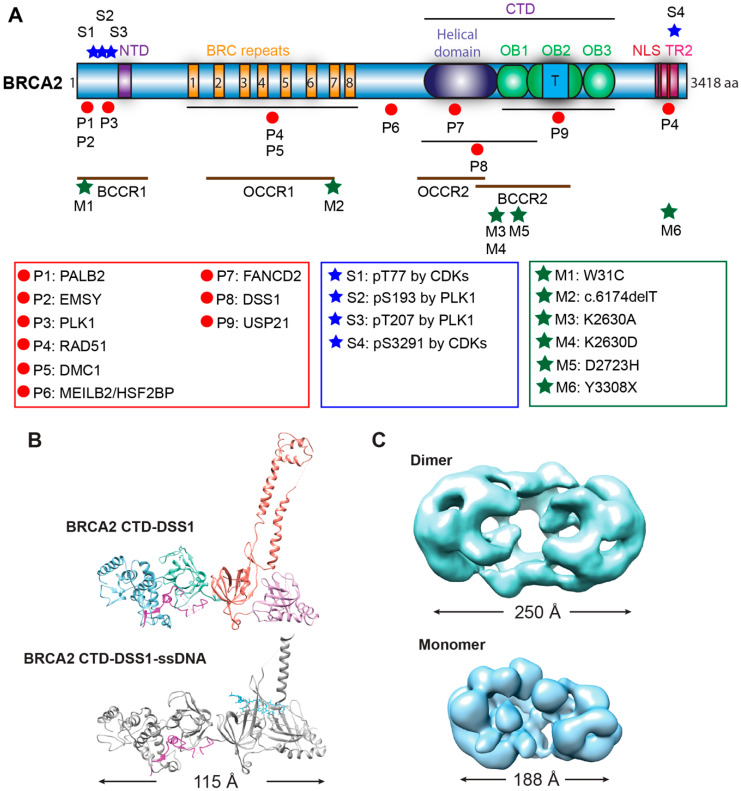
Figure 2.
Structure of BRCA2. (A) Domain structures with mapped sites for selected binding partners and phosphorylation. BRCA2 has two DNA-binding domains (N-terminal DNA-binding domain or NTD, C-terminal DNA-binding domain or CTD), eight BRC repeats interacting with RAD51 and DMC1, a C-terminal RAD51 interaction domain (TR2), and two nuclear localization signals (NLS). Mapped interaction sites with selected protein partners are indicated with red circles and listed in the red box [10,11,12,33,34,35,36,37,38,39,40,41,42]. Selected phosphorylation sites with blue stars and sites are listed in the blue box [35,36,43,44]. The proposed breast and ovarian cancer cluster regions (BCCR and OCCR) are labeled with brown lines [45,46]. Several common pathogenic mutations (ClinVar database) and loss-of-function mutations are marked by green stars and listed in the green box [34,47,48,49]. Abbreviation: aa, amino acid; OB fold, Oligonucleotide/Oligosaccharide-Binding fold; T, tower domain (three-helical bundle); P, binding protein; S, phosphorylation site; M, pathogenic mutation site; BCCR, breast cancer cluster region; OCCR, ovarian cancer cluster region. (B) Crystal structures of BRCA2 CTD in a complex with DSS1 alone (top, 1MIU) or with both DSS1 and ssDNA (bottom, 1MJE) [12]. (C) Low-resolution electron microscopic (EM) structures of the dimeric full-length BRCA2 (top, EMD-2779) [30] and the monomeric BRCA2-DSS1-ssDNA complex (bottom, EMD-21998) [23].