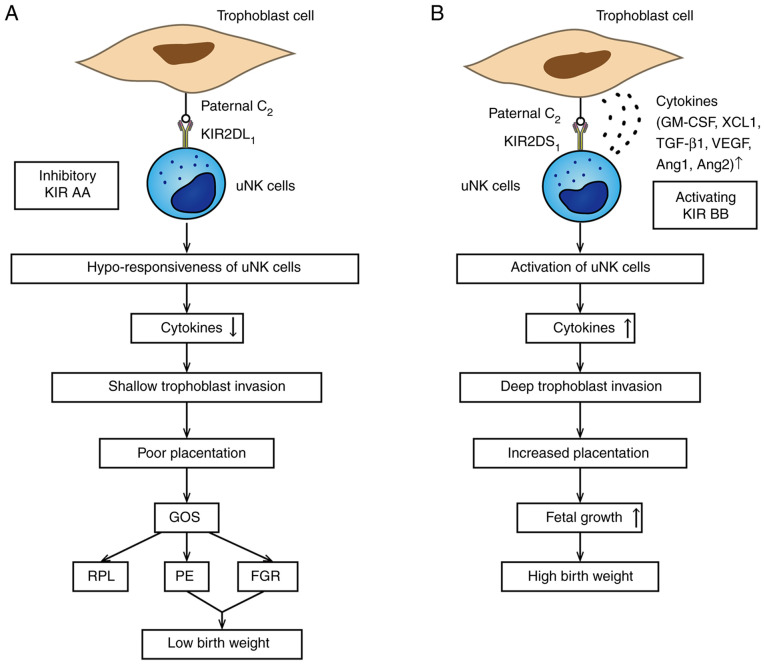
Figure 1.
Association between KIR/HLA-C combination and birth weight. (A) In this situation, the neonate inherits an HLA-C2 molecule from the father. The mother is KIR AA genotype; KIR2DL1 strongly combines to trophoblast HLA-C2 alleles leading to hypo-responsiveness of uNK cells, which is related to the poor placentation and leads to low birth weight in GOS. (B) Binding of KIR2DS1/HLA-C2 is associated with high birth weight. The KIR BB haplotype includes the activating KIR2DS1. Once this happens, uNK cells are activated to secrete plenty of cytokines, such as GM-CSF, which could enhance the placentation and lead to higher birth weight. KIR, killer-cell immunoglobulin-like receptor; HLA, human leukocyte antigen; uNK, uterine natural killer; GOS, great obstetrical syndromes; RPL, recurrent pregnancy loss; PE, preeclampsia; FGR, fetal growth restriction; GM-CSF, granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor; XCL1, chemokine C motif ligand 1; TGF-β1, transforming growth factor-β1; VEGF, vascular endothelial growth factor; Ang 1, angiopoietin 1.