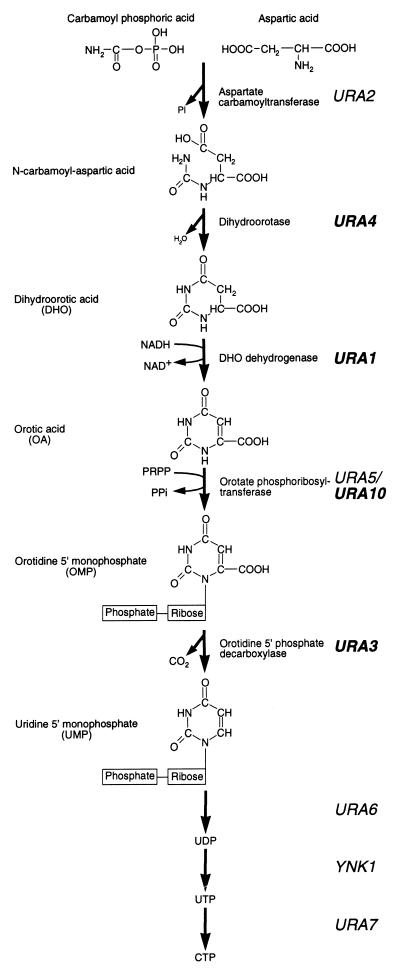
FIG. 1.
Pyrimidine biosynthetic pathway of S. cerevisiae. The pyrimidine ring is formed by the condensation of carbamoyl phosphoric acid and aspartic acid, followed by the elimination of a water molecule to form DHO. DHO is subsequently oxidized to OA by the product of the URA1 gene. A phosphoribose moiety, provided by 5-phosphoribose 1-pyrophosphate (PRPP), is added to OA to form OMP, which is then decarboxylated to form UMP by the product of the URA3 gene. UMP is subsequently converted to UDP and UTP before its conversion into CTP. Ppr1p is a transcriptional activator of the genes shown in bold typeface during conditions of pyrimidine starvation.