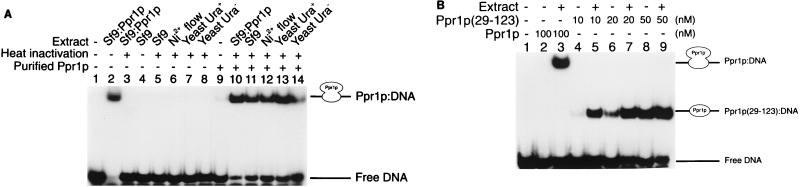
FIG. 3.
DNA binding properties of purified Ppr1p. (A) DNA binding by full-length Ppr1p. Electrophoretic mobility shift assays were performed as described in Materials and Methods. Reactions contained 32P-labelled DNA comprising a single Ppr1p binding site and, where indicated, 100 nM purified Ppr1p. The reactions were supplemented with cell extracts from Sf9 insect cells infected with a baculovirus producing Ppr1p (lanes 2, 3, and 10), Sf9 insect cells (lanes 4, 5, and 11), the flowthrough of a Ni2+-NTA column purification of Ppr1p from Sf9 insect cells infected with a baculovirus producing Ppr1p (lanes 6 and 12), or yeast cells (strain JPY5) grown in either medium containing uracil (lanes 7 and 13) or medium lacking uracil (lanes 8 and 14). Where indicated, the supplemented extract was placed in a boiling water bath for 5 min and centrifuged. The supernatant was then added to the binding reactions. Positions of the free DNA and the Ppr1p-DNA complex are indicated. (B) DNA binding properties of Ppr1p(29-123). Electrophoretic mobility shift assays were performed as described above, and Ppr1p or Ppr1p(29-123) was added at the concentrations indicated. Where indicated, a heat-treated extract of yeast cells (strain JPY5) was added to the reactions. Positions of the free DNA and the protein-DNA complexes are indicated.