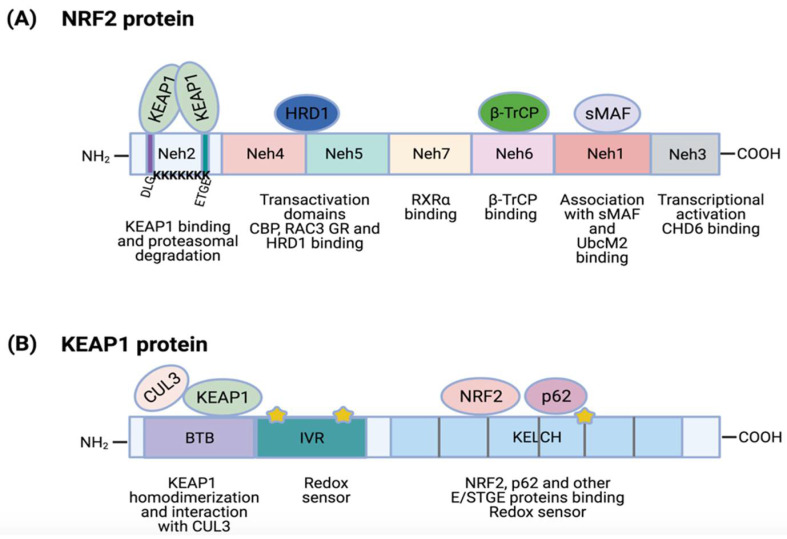
Figure 2.
NRF2 and KEAP1 protein structures. (A) NRF2 contains 7 highly conserved domains called Neh domains. Neh1 is required for complex formation with transcription factor sMAF, DNA binding and for binding to UbcM2. Neh2 contains ETGE and DLG sequences that are required for KEAP1 binding and 7 ubiquitin-lysine residues for targeting NRF2 for proteasomal degradation. Neh3 is needed for transcriptional activation (CHD6 binding). Neh4 and Neh5 are transactivation domains that bind activators (CBP, RAC3) or repressors (GR, HRD1). Neh6 regulates NRF2 stability by binding to β-TrCP. Finally, Neh7 can interact with RXRα, an NRF2 repressor; (B) KEAP1 protein contains 5 conserved regions: N-terminal region, BTB, IVR region, DGR domain and C-terminal region; DGR and C-terminal regions form a Kelch motif. The BTB domain facilitates KEAP1 homodimerization and CUL3 binding. The IVR region possesses a cysteine-rich domain that acts as a direct redox sensor. DGR/Kelch regions contains 6 repeats of a Kelch motif that mediate their interaction with NRF2 and other proteins with E/STGE conserved motifs, such as p62. This region also contains additional cysteine residues for stress sensing. Stars represent several cysteine residues located in IVR and Kelch domains.