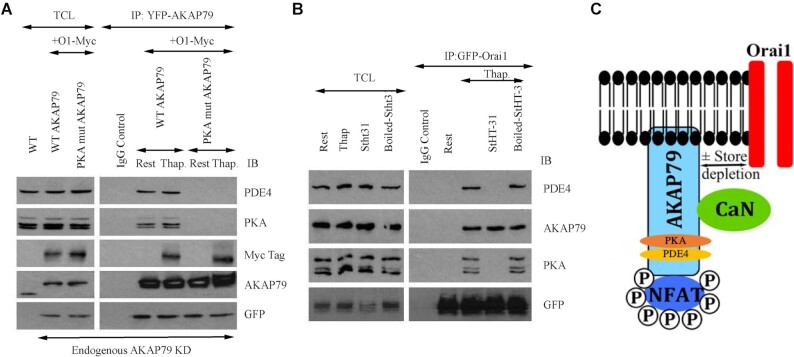
Figure 2.
PDE4 associates with AKAP79 in a protein kinase-dependent manner. (A) Pulldown of AKAP79-YFP revealed the presence of PDE4 and protein kinase A under resting conditions as well as myc-Orai1 after stimulation with thapsigargin. PDE4 and protein kinase A failed to associate with AKAP79 when a mutant AKAP protein was expressed that lacked the protein kinase A binding site (PKA mutant AKAP79). WT denotes wild type cells. AKAP79-YFP and PKA mutant AKAP79-YFP were expressed in cells in which endogenous AKAP79 had been knocked down using an siRNA-based approach. The row labelled AKAP79 reflects bands obtained with an anti-AKAP79 antibody. The GFP row shows the extent of YFP-tagged AKAP79 expression. (B) Immunoblots compare the association of endogenous PDE4, protein kinase A, and AKAP79 with GFP-tagged Orai1 in non-stimulated cells (Rest) and then after exposure to thapsigargin for 8 min. Cells were pre-treated with StHT-31 or boiled peptide for ∼15 min prior to stimulation with thapsigargin. In Panels A and B, rest and Thap groups were obtained in the presence of 2 mM external Ca2+-containing solution. (C) Cartoon depicts the presence of NFAT, calcineurin, protein kinase A (PKA) and PDE4 on AKAP79 and that the signalosome can interact with Orai1 following store depletion in a reversible manner. We do not know if PKA is present as the heterotetramer or as a single heterodimer. Previous work9 demonstrates that both regulatory and catalytic subunits of PKA are associated with AKAP79.