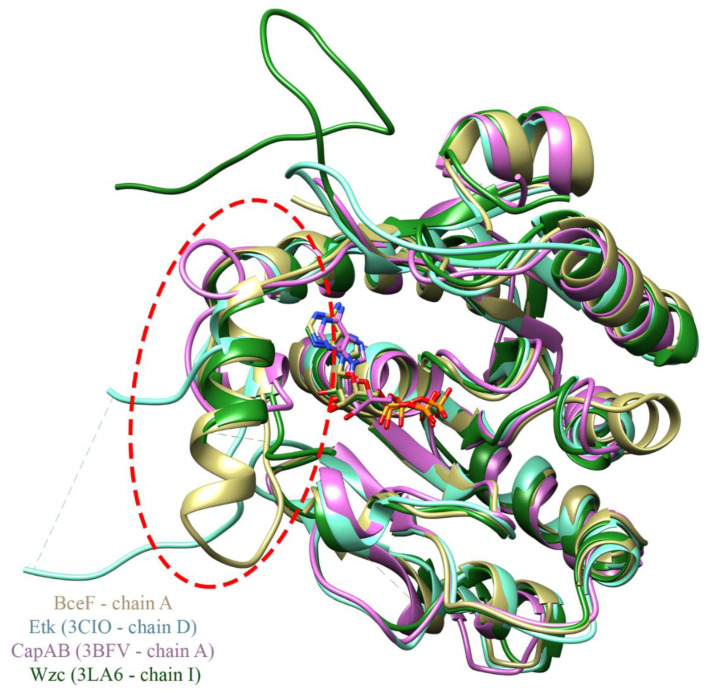
Figure 3.
Structural superimposition of the BceF, Etk, CapA/B, and Wzc kinase domains. Ribbon diagrams of the structure of BceF from B. cepacia colored in beige; Etk from E. coli in cyan (PDB: 3CIO [12]); CapA/B from S. aureus is purple (PDB: 3BFV [14]); Wzc from E. coli in dark green (PDB: 3LA6 [11]). Dashed lines represent regions that could not be resolved in the respective crystal structures. ADP, present in the crystal structure of BceF, CapA/B, and Wzc, is shown in balls and sticks and is colored by atom-type (beige, purple, and dark green carbons for the ADP from BceF, CapA/B, and Wzc, respectively). An evolutionary variable region (Figure 1) that is also structurally different between the kinases is evident on the utmost left side of the structures in this view, marked by a dashed red circle. The RMSD between BceF and Etk is 0.881 Å for 196 successfully aligned atom pairs, or “pruned” by the default criteria in Chimera [20], and 3.305 Å for all 238 pairs. The RMSD between BceF and CapA/B is 1.100 Å for 186 pruned atom pairs and 3.867 Å for all 232 pairs, and between BceF and Wzc is 0.885 Å for 208 pruned atom pairs and 1.930 Å for all 235 pairs.