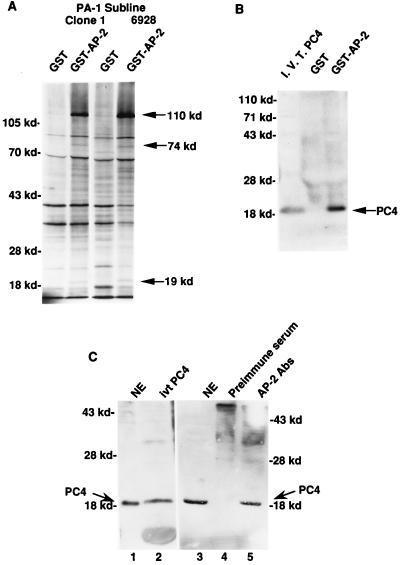
FIG. 1.
Physical interaction between AP-2 and PC4. (A) Physical interaction between GST–AP-2 and proteins from PA-1 cell nuclear extracts. The GST–AP-2 fusion protein binding assays were performed as described in Materials and Methods. Nuclear extracts prepared from metabolically 35S-labeled PA-1 cells contain at least three polypeptides that specifically interact with AP-2. The polypeptides (110, 74, and 19 kDa) are marked at the right. The mobilities of the molecular markers are indicated on the left (in kilodaltons). Clone 1, a subline of PA-1; 6928, a ras oncogene-transfected clone 1 line. (B) Physical interaction between GST–AP-2 and PC4. Four-milligram quantities of unlabeled PA-1 nuclear extracts were used in these assays, and the GST–AP-2-bound proteins were electrophoresed and transferred to a nitrocellulose membrane. The membrane was probed with an antiserum raised against PC4. The mobilities of the molecular markers are indicated at the left (in kilodaltons). The 19-kDa PC4 protein is marked on the right. I.V.T. PC4, in vitro-translated PC4 protein. (C) Physical interaction of AP-2 and PC4 in PA-1 cells. Four-milligram quantities of PA-1 cell nuclear extracts were treated with AP-2-specific antibodies and analyzed for coimmunoprecipitation of PC4 as described in Materials and Methods. The molecular markers are shown on the left and on the right (in kilodaltons). The smear in lanes 4 and 5 occurred because of the immunoglobulin molecules used for immunoprecipitation. Lanes: 1, PA-1 cell nuclear extract (NE), 50 μg; 2, in vitro-translated (ivt) PC4 protein; 3, NE, 50 μg; 4, preimmune serum; 5, anti-AP-2 antibodies (Abs).