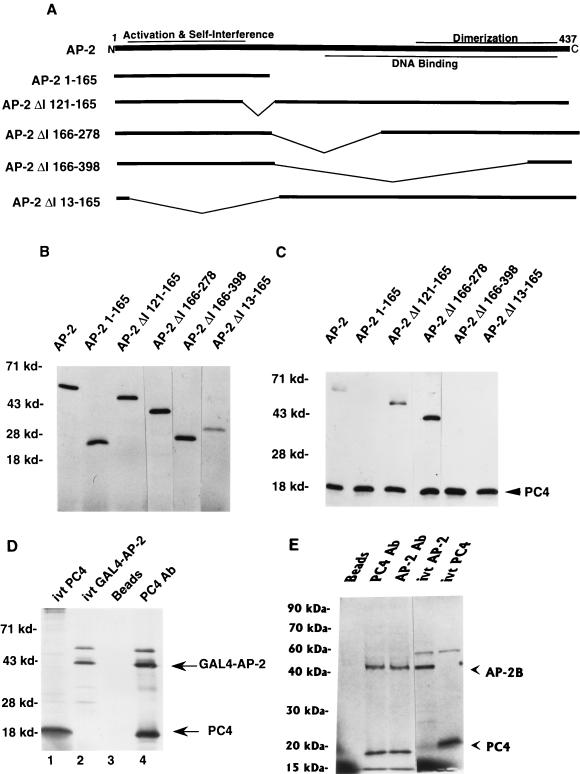
FIG. 2.
Activation domain of AP-2 interacts with PC4. AP-2, GAL4–AP-2, AP-2B, and PC4 proteins were synthesized by using a TNT T7 polymerase kit as described in Materials and Methods. (A) Deletion mutants of AP-2 used for coimmunoprecipitation with PC4. Functional regions on the AP-2 protein that have been characterized are shown on the full-length AP-2 molecule. (B) In vitro-translated AP-2 proteins. AP-2 proteins were synthesized in vitro and separated on an SDS–10% polyacrylamide gel. The panel with the wild-type AP-2 protein contains one-fifth of the amount of input protein that was used for coimmunoprecipitation. The mobilities of molecular markers are indicated at the left (in kilodaltons). (C) Coimmunoprecipitation of PC4 and various deletion mutants of AP-2. Coimmunoprecipitation studies were carried out with PC4 antiserum as described in Materials and Methods. The immunoprecipitated proteins were separated on an SDS–15% polyacrylamide gel. The molecular markers are shown on the left, and the PC4 protein is indicated on the right. (D and E) Physical interaction of PC4 and the GAL4–AP-2 fusion protein (D) or AP-2B (E). The experiments were carried out as described in Materials and Methods. For in vitro-translated (ivt) PC4, ivt GAL4–AP-2, and ivt–AP-2; one-fifth of the amounts of their respective proteins that were used in immunoprecipitation assays were employed. The molecular markers are shown at the left, and the GAL4–AP-2, AP-2B, and PC4 proteins are indicated on the right.