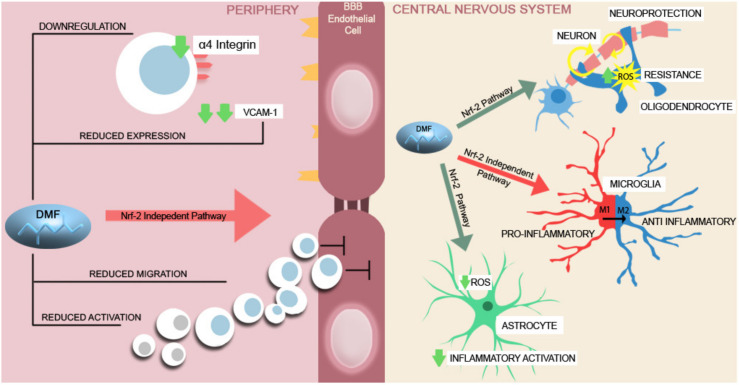
Figure 2.
A brief schematic representation of DMF’s mechanism of action. In the peripheral compartment, DMF induces changes in the immune response by decreasing the activation and migration of Th lymphocytes. It further alters the transendothelial migration across the BBB, reduces the expression of the adhesion molecules, such as VCAM-1, and downregulates the α4 integrin on the lymphocyte surface [81,82,84,85,88,89]. Inside the CNS, DMF carries Nrf-2 dependent neuroprotective effects upon the neurons and oligodendrocytes by increasing the ROS resistance of the neurons and glial cells and upon the astrocytes by decreasing the proinflammatory cytokine secretion and intracellular ROS production [86,90,91]. In proinflammatory activated microglia, DMF reduces the production of proinflammatory mediators and stimulates the shift from a M1 proinflammatory state to a M2, anti-inflammatory state [86,92].