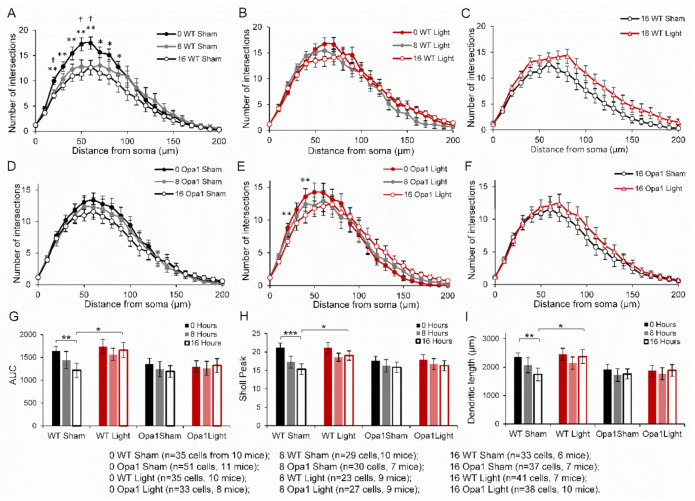
Figure 2.
In vivo 670 nm pretreatment inhibited the axotomy-related dendropathy that occurred in sham-treated WT over 16 h following axotomy. Sholl profiles of (A) sham-treated aged WT RGCs showed significant degeneration over time post axotomy. (B) no effects were observed in light-treated WT RGCs. (C) Direct comparison of sham vs. light treatment following 16 h ex vivo. WT RGCs; (D) Sham- and (E) light-treated Opa1+/− RGC Sholl curves showed no significant degeneration ex vivo. (F) a direct comparison of the two 16-h Opa1+/− groups showed no significant effects. RGC dendritic complexity was also quantified by (G) the area under the Sholl curve (AUC); (H) average maximum peak of Sholl curve; and (I) average total dendritic length. All measures revealed significant degeneration over 16 h in the sham-treated WT RGCs, which was inhibited by the light treatment, as shown by the 16-h WT light group having significantly greater dendritic complexity. Daggers and stars indicate a statistically significant reduction in the number of dendritic intersections from 0 h to 8- and 16-h, respectively. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, † p < 0.05; Mann-Whitney U-test. Error bars represent SEM.